Characterization and evaluation of the enzymatic activity of tetanus toxin submitted to cobalt-60 gamma radiation
- PMID: 33995513
- PMCID: PMC8092855
- DOI: 10.1590/1678-9199-JVATITD-2020-0140
Characterization and evaluation of the enzymatic activity of tetanus toxin submitted to cobalt-60 gamma radiation
Abstract
Background: Tetanus toxin blocks the release of the inhibitory neurotransmitters in the central nervous system and causes tetanus and its main form of prevention is through vaccination. The vaccine is produced by inactivation of tetanus toxin with formaldehyde, which may cause side effects. An alternative way is the use of ionizing radiation for inactivation of the toxin and also to improve the potential immunogenic response and to reduce the post-vaccination side effects. Therefore, the aim of this study was to characterize the tetanus toxin structure after different doses of ionizing radiation of 60Co.
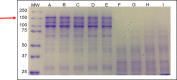
Methods: Irradiated and native tetanus toxin was characterized by SDS PAGE in reducing and non-reducing conditions and MALD-TOF. Enzymatic activity was measured by FRET substrate. Also, antigenic properties were assessed by ELISA and Western Blot data.
Results: Characterization analysis revealed gradual modification on the tetanus toxin structure according to doses increase. Also, fragmentation and possible aggregations of the protein fragments were observed in higher doses. In the analysis of peptide preservation by enzymatic digestion and mass spectrometry, there was a slight modification in the identification up to the dose of 4 kGy. At subsequent doses, peptide identification was minimal. The analysis of the enzymatic activity by fluorescence showed 35 % attenuation in the activity even at higher doses. In the antigenic evaluation, anti-tetanus toxin antibodies were detected against the irradiated toxins at the different doses, with a gradual decrease as the dose increased, but remaining at satisfactory levels.
Conclusion: Ionizing radiation promoted structural changes in the tetanus toxin such as fragmentation and/or aggregation and attenuation of enzymatic activity as the dose increased, but antigenic recognition of the toxin remained at good levels indicating its possible use as an immunogen. However, studies of enzymatic activity of tetanus toxin irradiated with doses above 8 kGy should be further analyzed.
Keywords: Enzymatic activity; Fragmentation; Gamma rays; Radiation.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Enzymatic fragmentation of tetanus toxin. Identification and characterization of an atoxic, immunogenic fragment.Mol Cell Biochem. 1978 Oct 13;21(1):23-31. doi: 10.1007/BF00230193. Mol Cell Biochem. 1978. PMID: 104144
-
Enzymatic hydrolysis of tetanus toxin by intrinsic and extrinsic proteases. Characterization of the fragments by monoclonal antibodies.Med Microbiol Immunol. 1985;174(3):139-50. doi: 10.1007/BF02298124. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1985. PMID: 3897815
-
[Effect of gamma radiation on the immunobiological and immunochemical properties of cholera exotoxin. I. Change in the biological activity of nonpurified cholera exotoxin as affected by ionizing radiation].Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1984 Feb;(2):47-51. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1984. PMID: 6711194 Russian.
-
Reduced-antigen, combined diphtheria, tetanus and acellular pertussis vaccine, adsorbed (Boostrix®): a review of its properties and use as a single-dose booster immunization.Drugs. 2012 Sep 10;72(13):1765-91. doi: 10.2165/11209630-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22931522 Review.
-
Tetanus Toxin Fragment C: Structure, Drug Discovery Research and Production.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jun 17;15(6):756. doi: 10.3390/ph15060756. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35745675 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Irradiated oocysts in combination with inulin adjuvant-induced potent immune responses against Eimeria tenella infection in broiler chickens.Vet Res Forum. 2023;14(8):423-429. doi: 10.30466/vrf.2023.563143.3675. Epub 2023 Aug 15. Vet Res Forum. 2023. PMID: 37667788 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Irradiated Livestock Vaccine Research and Production Addressing the Unmet Needs for Farmers and Veterinary Services in FAO/IAEA Member States.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 28;13:853874. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.853874. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35418985 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stock I. Tetanus and Clostridium tetani-a brief review. Med Monatsschr Pharm. 2015;38(2):57–60. - PubMed
-
- Vollman KE, Acquisto NM, Bodkin RP. A case of tetanus infection in an adult with a protective tetanus antibody level. Am J Emerg Med. 2014;32(4):392.e3–392.e4. - PubMed
-
- Papadiochos I, Papadiochou S, Petsinis V, Goutzanis L, Atsali C, Papadogeorgaki N. Trismus as a Clinical Manifestation of Tetanus: A Case Report. J Oral Facial Pain Headache. 2016;30(4):355–362. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
