Prospective of extracellular matrix and drug correlations in disease management
- PMID: 33995610
- PMCID: PMC8105415
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajps.2020.06.007
Prospective of extracellular matrix and drug correlations in disease management
Abstract
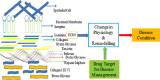
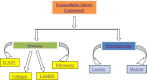
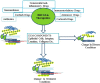
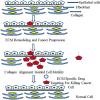
The extracellular matrix (ECM) comprises of many structural molecules that constitute the extracellular environment. ECM molecules are characterized by specific features like diversity, complexity and signaling, which are also results of improvement or development of disease mediated by some physiological changes. Several drugs have also been used to manage diseases and they have been reported to modulate ECM assembly, including physiological changes, beyond their primary targets and ECM metabolism. This review highlights the alteration of ECM environment for diseases and effect of different classes of drugs like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, immune suppressant drug, steroids on ECM or its components. Thus, it is summarized from previously conducted researches that diseases can be managed by targeting specific components of ECM which are involved in the pathophysiology of diseases. Moreover, the drug delivery focused on targeting the ECM components also has the potential for the discovery of targeted and site specific release of drugs. Therefore, ECM or its components could be future targets for the development of new drugs for controlling various disease conditions including neurodegenerative diseases and cancers.
Keywords: Disease; Drug target; Extracellular matrix; Pharmacotherapeutics.
© 2020 Shenyang Pharmaceutical University. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular matrix molecules: potential targets in pharmacotherapy.Pharmacol Rev. 2009 Jun;61(2):198-223. doi: 10.1124/pr.109.001289. Pharmacol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19549927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Matrix Macromolecules as Potential Targets of Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy.Adv Pharmacol. 2018;81:209-240. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2017.09.008. Adv Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29310799 Review.
-
Targeting the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix in cardiovascular disease drug discovery.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2022 May;17(5):443-460. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2022.2047645. Epub 2022 Mar 8. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2022. PMID: 35258387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular matrix in uterine leiomyoma pathogenesis: a potential target for future therapeutics.Hum Reprod Update. 2018 Jan 1;24(1):59-85. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmx032. Hum Reprod Update. 2018. PMID: 29186429 Review.
-
Modeling and measuring extracellular matrix alterations in fibrosis: challenges and perspectives for antifibrotic drug discovery.Connect Tissue Res. 2019 Jan;60(1):62-70. doi: 10.1080/03008207.2018.1500557. Epub 2018 Aug 3. Connect Tissue Res. 2019. PMID: 30071759 Review.
Cited by
-
Rescue of mitochondrial dysfunction through alteration of extracellular matrix composition in barth syndrome cardiac fibroblasts.Biomaterials. 2025 Apr;315:122922. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122922. Epub 2024 Oct 26. Biomaterials. 2025. PMID: 39509858
-
Mass spectrometry methods for analysis of extracellular matrix components in neurological diseases.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2023 Sep-Oct;42(5):1848-1875. doi: 10.1002/mas.21792. Epub 2022 Jun 20. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2023. PMID: 35719114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
USP10 Promotes Fibronectin Recycling, Secretion, and Organization.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Oct 4;62(13):15. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.13.15. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 34665194 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Matrix Signaling Cues: Biological Functions, Diseases, and Therapeutic Targets.MedComm (2020). 2025 Jul 17;6(8):e70281. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70281. eCollection 2025 Aug. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40686923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of doxorubicin as a potential therapeutic against SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) protease: a molecular docking and dynamics simulation studies.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022 Oct;40(17):7960-7974. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2021.1905551. Epub 2021 Apr 7. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022. PMID: 33826483 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

