Application of regenerative medicine to salivary gland hypofunction
- PMID: 33995711
- PMCID: PMC8102160
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jdsr.2021.03.002
Application of regenerative medicine to salivary gland hypofunction
Abstract
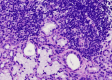
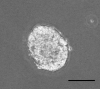
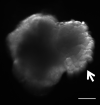
Dry mouth results from hypofunction of the salivary glands due to Sjögren's syndrome (SS), various medications, and radiation therapy for head and neck cancer. In severe cases of salivary gland hypofunction, sialagogues are not always effective due to the loss of salivary parenchyma. Therefore, regenerative medicine using stem cell therapy is a promising treatment for severe cases. Stem cells are classified into three groups: tissue stem cells, embryonic stem cells, and induced pluripotent stem cells. Tissue stem cells, such as hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and salivary stem/progenitor cells, could rescue irradiation-induced salivary gland hypofunction. Both HSCs and MSCs can rescue salivary gland hypofunction through soluble factors in a paracrine manner, while salivary stem/progenitor cells can reconstitute the damaged salivary glands. In fact, we clarified that CD133-positive cells in mouse submandibular glands showed stem cell features, which reconstituted the damaged salivary glands. Furthermore, we focused on the challenge of producing functional salivary glands that are three-dimensionally induced from mouse ES cells.
Keywords: Cell therapy; Organoid; Regenerative medicine; Salivary gland hypofunction; Stem cells.
© 2021 The Authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In vitro three-dimensional culture systems of salivary glands.Pathol Int. 2020 Aug;70(8):493-501. doi: 10.1111/pin.12947. Epub 2020 May 4. Pathol Int. 2020. PMID: 32367629
-
Current developments and opportunities of pluripotent stem cells-based therapies for salivary gland hypofunction.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jan 19;12:1346996. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1346996. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38313227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characteristics of Labial Gland Mesenchymal Stem Cells of Healthy Individuals and Patients with Sjögren's Syndrome: A Preliminary Study.Stem Cells Dev. 2017 Aug 15;26(16):1171-1185. doi: 10.1089/scd.2017.0045. Epub 2017 Jun 26. Stem Cells Dev. 2017. PMID: 28537471
-
Salivary Gland Hypofunction and Xerostomia in Head and Neck Radiation Patients.J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 2019 Aug 1;2019(53):lgz016. doi: 10.1093/jncimonographs/lgz016. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 2019. PMID: 31425600 Review.
-
Generation of functional salivary gland tissue from human submandibular gland stem/progenitor cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 Mar 20;11(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01628-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32197647 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Autologous mesenchymal stem cells offer a new paradigm for salivary gland regeneration.Int J Oral Sci. 2023 May 10;15(1):18. doi: 10.1038/s41368-023-00224-5. Int J Oral Sci. 2023. PMID: 37165024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gingival-derived mesenchymal stem cell therapy regenerated the radiated salivary glands: functional and histological evidence in murine model.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Feb 16;15(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03659-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38365799 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular matrix turnover in salivary gland disorders and regenerative therapies: Obstacles and opportunities.J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2023 Nov-Dec;13(6):693-703. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2023.08.009. Epub 2023 Sep 12. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2023. PMID: 37719063 Free PMC article.
-
Atrophy and Inflammatory Changes in Salivary Glands Induced by Oxidative Stress after Exposure to Drugs and Other Chemical Substances: A Systematic Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Sep 21;59(9):1692. doi: 10.3390/medicina59091692. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37763811 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-Free Therapies: The Use of Cell Extracts to Mitigate Irradiation-Injured Salivary Glands.Biology (Basel). 2023 Feb 14;12(2):305. doi: 10.3390/biology12020305. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829582 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Guggenheimer J., Moore P.A. Xerostomia: etiology, recognition and treatment. J Am Dent Assoc. 2003;134:61–69. quiz 118-9. - PubMed
-
- Smith C.H., Boland B., Daureeawoo Y., Donaldson E., Small K., Tuomainen J. Effect of aging on stimulated salivary flow in adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013;61:805–808. - PubMed
-
- Sreebny L., Chambers M.S., Fleming T.J., Martin J.W., Toth B.B. Xerostomia: managing a complex condition. Interview by Phillip Bonner. Dent Today. 1997;16:66–67. 86-87. - PubMed
-
- Frydrych A.M., Davies G.R., Slack-Smith L.M., Heywood J. An investigation into the use of pilocarpine as a sialagogue in patients with radiation induced xerostomia. Aust Dent J. 2002;47:249–253. - PubMed
-
- Eisbruch A., Ten Haken R.K., Kim H.M., Marsh L.H., Ship J.A. Dose, volume, and function relationships in parotid salivary glands following conformal and intensity-modulated irradiation of head and neck cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999;45:577–587. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

