Exploring the Role and Mechanism of pAMPK α-Mediated Dysregulation of Brf1 and RNA Pol III Genes
- PMID: 33995823
- PMCID: PMC8081602
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5554932
Exploring the Role and Mechanism of pAMPK α-Mediated Dysregulation of Brf1 and RNA Pol III Genes
Abstract
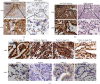
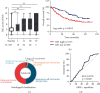
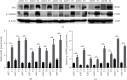
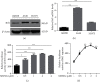
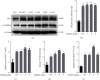
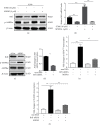
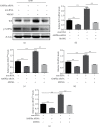
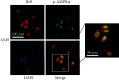
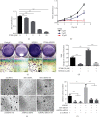
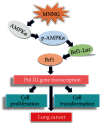
TF IIB-related factor 1 (Brf1) is a key transcription factor of RNA polymerase III (Pol III) genes. Our early studies have demonstrated that Brf1 and Pol III genes are epigenetically modulated by histone H3 phosphorylation. Here, we have further investigated the relationship of the abnormal expression of Brf1 with a high level of phosphorylated AMPKα (pAMPKα) and explored the role and molecular mechanism of pAMPKα-mediated dysregulation of Brf1 and Pol III genes in lung cancer. Brf1 is significantly overexpressed in lung cancer cases. The cases with high Brf1 expression display short overall survival times. Elevation of Brf1 expression is accompanied by a high level of pAMPKα. Brf1 and pAMPKα colocalize in nuclei. Further analysis indicates that the carcinogen MNNG induces pAMPKα to upregulate Brf1 expression, resulting in the enhancement of Pol III transcription. In contrast, inhibiting pAMPKα decreases cellular levels of Brf1, resulting in the reduction of Pol III gene transcription to attenuate the rates of cell proliferation and colony formation of lung cancer cells. These outcomes demonstrate that high Brf1 expression reveals a worse prognosis in lung cancer patients. pAMPKα-mediated dysregulation of Brf1 and Pol III genes plays important roles in cell proliferation, colony formation, and tumor development of lung cancer. Brf1 may be a biomarker for establishing the prognosis of lung cancer. It is a new mechanism that pAMPKα mediates dysregulation of Brf1 and Pol III genes to promote lung cancer development.
Copyright © 2021 Teng Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ROS Signaling-Mediated Novel Biological Targets: Brf1 and RNA Pol III Genes.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Oct 4;2021:5888432. doi: 10.1155/2021/5888432. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. Retraction in: Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2024 Jan 9;2024:9890237. doi: 10.1155/2024/9890237. PMID: 34646425 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
The significance of Runx2 mediating alcohol-induced Brf1 expression and RNA Pol III gene transcription.Chem Biol Interact. 2020 May 25;323:109057. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2020.109057. Epub 2020 Mar 18. Chem Biol Interact. 2020. PMID: 32198086 Free PMC article.
-
Role of phosphorylated histone H3 serine 10 in DEN-induced deregulation of Pol III genes and cell proliferation and transformation.Carcinogenesis. 2013 Nov;34(11):2460-9. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt219. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Carcinogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23774401 Free PMC article.
-
Tamoxifen represses alcohol-induced transcription of RNA polymerase III-dependent genes in breast cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2014 Dec 15;5(23):12410-7. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2678. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25400119 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol Intake and Abnormal Expression of Brf1 in Breast Cancer.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Oct 31;2019:4818106. doi: 10.1155/2019/4818106. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31781337 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ROS Signaling-Mediated Novel Biological Targets: Brf1 and RNA Pol III Genes.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Oct 4;2021:5888432. doi: 10.1155/2021/5888432. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. Retraction in: Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2024 Jan 9;2024:9890237. doi: 10.1155/2024/9890237. PMID: 34646425 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
Downregulation of Brf1 Induces Liver Failure and Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Promoting Apoptosis.J Cancer. 2024 Sep 3;15(17):5577-5593. doi: 10.7150/jca.97277. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39308682 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu Y. L., Cheng Y., Zhou X., et al. Dacomitinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment for patients with _EGFR_ -mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ARCHER 1050): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. The Lancet Oncology. 2017;18(11):1454–1466. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30608-3. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

