Polydatin Attenuates OGD/R-Induced Neuronal Injury and Spinal Cord Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Protecting Mitochondrial Function via Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 33995825
- PMCID: PMC8081604
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6687212
Polydatin Attenuates OGD/R-Induced Neuronal Injury and Spinal Cord Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Protecting Mitochondrial Function via Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathway
Abstract
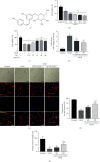
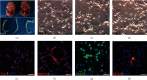
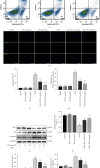
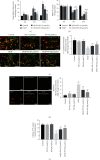
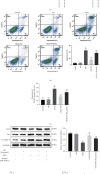
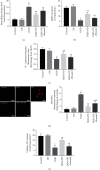
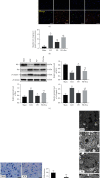
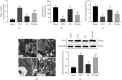
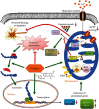
Spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury (SCII) is a devastating complication of spinal or thoracic surgical procedures and can lead to paraplegia or quadriplegia. Neuronal cell damage involving mitochondrial dysfunction plays an important role in the pathogenesis of SCII. Despite the availability of various treatment options, there are currently no mitochondria-targeting drugs that have proven effective against SCII. Polydatin (PD), a glucoside of resveratrol, is known to preserve mitochondrial function in central nervous system (CNS) diseases. The aim of the present study was to explore the neuro- and mito-protective functions of PD and its underlying mechanisms. An in vitro model of SCII was established by exposing spinal cord motor neurons (SMNs) to oxygen-glucose-deprivation/reperfusion (OGD/R), and the cells were treated with different dosages of PD for varying durations. PD improved neuronal viability and protected against OGD/R-induced apoptosis and mitochondrial injury in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, PD restored the activity of neuronal mitochondria in terms of mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), intracellular calcium levels, mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) opening, generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) levels. Mechanistically, PD downregulated Keap1 and upregulated Nrf2, NQO-1, and HO-1 in the OGD/R-treated SMNs. Likewise, PD treatment also reversed the neuronal and mitochondrial damage induced by SCII in a mouse model. Furthermore, the protective effects of PD were partially blocked by the Nrf2 inhibitor. Taken together, PD relieves mitochondrial dysfunction-induced neuronal cell damage by activating the Nrf2/ARE pathway and is a suitable therapeutic option for SCII.
Copyright © 2021 Jiheng Zhan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Li X. Q., Chen F. S., Tan W. F., Fang B., Zhang Z. L., Ma H. Elevated microRNA-129-5p level ameliorates neuroinflammation and blood-spinal cord barrier damage after ischemia-reperfusion by inhibiting HMGB1 and the TLR3-cytokine pathway. Journal of Neuroinflammation. 2017;14(1):p. 205. doi: 10.1186/s12974-017-0977-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

