High Velocity Gunshot Fractures of Humerus: Results of Primary Plate Osteosynthesis
- PMID: 33995878
- PMCID: PMC8081774
- DOI: 10.1007/s43465-020-00299-w
High Velocity Gunshot Fractures of Humerus: Results of Primary Plate Osteosynthesis
Abstract
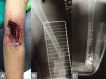
Background: High velocity gunshot fractures usually seen in conflict zones, often mandate external fixation due to delayed presentation and associated contamination. In the presented observational study, we managed high velocity gunshot fractures of humerus with adequate debridement and primary plate osteosynthesis under controlled conditions with gratifying results.
Material and methods: Eighteen consecutive cases of fracture of the humerus secondary to high velocity gunshot wounds with ages ranging from 28 to 45 years reporting within 6 h of the initial injury formed our study group. Immediate debridement, lavage and primary plate osteosynthesis was carried out following hemodynamic stabilisation and intravenous antibiotics. All the cases were followed up at 2, 4, 6 months, 1 year and then annual follow-up including telephonic follow-up for six patients.
Results: Fifteen cases of Gustillo Anderson type III A, two of type III B and one of type III C were managed with primary plate osteosynthesis. Brachial artery injury was addressed immediately, however injured radial nerve ends were tagged. Five cases showed delayed/non-union and were managed with decortication and autologous bone grafting. Two cases of deep infection could be managed with implant retention till union. The implants were removed following fracture consolidation. All the fractures united and no patient was left with sequelae of chronic infection.
Conclusion: Timely presentation of high velocity gunshot fractures of humerus teamed up with adequate debridement, soft tissue management and primary plate osteosynthesis can offer satisfactory outcomes. Associated vascular injury needs immediate attention. Nerve injuries can be addressed in a staged procedure. Our results have been satisfactory and add to the scant literature available on the subject, however further studies are warranted.
Keywords: Gunshot; Humerus; Internal fixation; Open fracture.
© Indian Orthopaedics Association 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestManoj Kumar, J. P. Khatri and C. M. Singh declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Primary internal fixation in open fractures of tibia following high-velocity gunshot wounds: a single-centre experience.Int Orthop. 2020 Apr;44(4):685-691. doi: 10.1007/s00264-019-04387-x. Epub 2019 Aug 7. Int Orthop. 2020. PMID: 31392496
-
Staged minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of proximal tibial fractures with acute compartment syndrome.Injury. 2017 Jun;48(6):1190-1193. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2017.03.010. Epub 2017 Mar 11. Injury. 2017. PMID: 28320508
-
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for open fractures of the proximal tibia.Clin Orthop Surg. 2012 Dec;4(4):313-20. doi: 10.4055/cios.2012.4.4.313. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Clin Orthop Surg. 2012. PMID: 23205242 Free PMC article.
-
[Periprosthetic humeral fractures: from osteosynthesis to prosthetic replacement].Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2019 Apr;31(2):84-97. doi: 10.1007/s00064-019-0591-y. Epub 2019 Feb 28. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2019. PMID: 30820585 Review. German.
-
[Fractures of the shaft of the humerus: systematic plate fixation. Anatomic and functional results in 156 cases and a review of the literature].Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2000 Jun;86(4):346-59. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2000. PMID: 10880934 Review. French.
References
-
- Chapman MW, Mahoney M. The role of early internal fixation in the management of open fractures. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 1979;138:120–131. - PubMed
-
- Eastman JR. Gunshot fractures of the shaft of the humerus. JAMA. 1917;LXIX:251–256. doi: 10.1001/jama.1917.02590310003002. - DOI
-
- Dougherty PJ, Soheil N. Gunshot humerus shaft fractures. Techniques in Orthopaedics. 2006;21:214–217. doi: 10.1097/01.bto.0000240297.49428.d7. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
