Structural modeling of a novel membrane-bound globin-coupled sensor in Geobacter sulfurreducens
- PMID: 33995893
- PMCID: PMC8076648
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.03.031
Structural modeling of a novel membrane-bound globin-coupled sensor in Geobacter sulfurreducens
Abstract
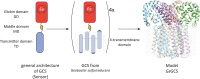
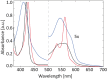
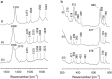
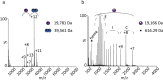
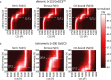
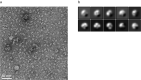
Globin-coupled sensors (GCS) usually consist of three domains: a sensor/globin, a linker, and a transmitter domain. The globin domain (GD), activated by ligand binding and/or redox change, induces an intramolecular signal transduction resulting in a response of the transmitter domain. Depending on the nature of the transmitter domain, GCSs can have different activities and functions, including adenylate and di-guanylate cyclase, histidine kinase activity, aerotaxis and/or oxygen sensing function. The gram-negative delta-proteobacterium Geobacter sulfurreducens expresses a protein with a GD covalently linked to a four transmembrane domain, classified, by sequence similarity, as GCS (GsGCS). While its GD is fully characterized, not so its transmembrane domain, which is rarely found in the globin superfamily. In the present work, GsGCS was characterized spectroscopically and by native ion mobility-mass spectrometry in combination with cryo-electron microscopy. Although lacking high resolution, the oligomeric state and the electron density map were valuable for further rational modeling of the full-length GsGCS structure. This model demonstrates that GsGCS forms a transmembrane domain-driven tetramer with minimal contact between the GDs and with the heme groups oriented outward. This organization makes an intramolecular signal transduction less likely. Our results, including the auto-oxidation rate and redox potential, suggest a potential role for GsGCS as redox sensor or in a membrane-bound e-/H+ transfer. As such, GsGCS might act as a player in connecting energy production to the oxidation of organic compounds and metal reduction. Database searches indicate that GDs linked to a four or seven helices transmembrane domain occur more frequently than expected.
Keywords: AfGcHK, Anaeromyxobacter sp. Fw109-5 GcHK; AsFRMF, Ascaris suum FRMF-amide receptor; AvGReg, Azotobacter vinilandii Greg; BpGReg, Bordetella pertussis Greg; BsHemAT, Bacillus subtilis HemAT; CCS, collision cross section; CIU, collision-induced unfolding; CMC, critical micelle concentration; CV, cyclic voltammetry; CeGLB26, Caenorhabditis elegans globin 26; CeGLB33, Caenorhabditis elegans globin 33; CeGLB6, Caenorhabditis elegans globin 6; DDM, n-dodecyl-β-d-maltoside; DPV, differential pulse voltammetry; EcDosC, Escherichia coli Dos with DGC activity; FMRF, H-Phe-Met-Arg-Phe-NH2 neuropeptide; GCS, globin-coupled sensor; GD, globin domain; GGDEF, Gly-Gly-Asp-Glu-Phe motive; Gb, globin; Geobacter sulfurreducens; GintHb, hemoglobin from Gasterophilus intestinalis; Globin-coupled sensor; GsGCS, Geobacter sulfurreducens GCS; GsGCS162, GD of GsGCS; IM-MS, ion mobility-mass spectrometry; LmHemAC, Leishmania major HemAC; MaPgb, Methanosarcina acetivorans protoglobin; MtTrHbO, Mycobacterium tuberculosis truncated hemoglobin O; NH4OAc, ammonium acetate; OG, n-octyl-β-d-glucopyranoside; PDE, phosphodiesterase; PcMb, Physether catodon myoglobin; PccGCS, Pectobacterium carotivorum GCS; PsiE, phosphate-starvation-inducible E; RR, resonance Raman; SCE, saturated calomel electrode; SHE, standard hydrogen electrode; SaktrHb, Streptomyces avermitilis truncated hemoglobin-antibiotic monooxygenase; SwMb, myoglobin from sperm whale; TD, Transmitter domain; TmD, Transmembrane domain; Transmembrane domain; Transmembrane-coupled globins; mNgb, mouse neuroglobin.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


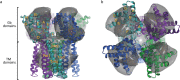
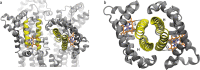
Similar articles
-
The heme pocket of the globin domain of the globin-coupled sensor of Geobacter sulfurreducens--an EPR study.J Inorg Biochem. 2010 Oct;104(10):1022-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2010.05.009. Epub 2010 May 16. J Inorg Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20605218
-
A globin domain in a neuronal transmembrane receptor of Caenorhabditis elegans and Ascaris suum: molecular modeling and functional properties.J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 17;290(16):10336-52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.576520. Epub 2015 Feb 9. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25666609 Free PMC article.
-
HisE11 and HisF8 provide bis-histidyl heme hexa-coordination in the globin domain of Geobacter sulfurreducens globin-coupled sensor.J Mol Biol. 2009 Feb 13;386(1):246-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.12.023. Epub 2008 Dec 16. J Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19109973
-
Signal transduction mechanisms in heme-based globin-coupled oxygen sensors with a focus on a histidine kinase (AfGcHK) and a diguanylate cyclase (YddV or EcDosC).Biol Chem. 2022 Sep 27;403(11-12):1031-1042. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2022-0185. Print 2022 Nov 25. Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 36165459 Review.
-
Protoglobin: structure and ligand-binding properties.Adv Microb Physiol. 2013;63:79-96. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407693-8.00003-0. Adv Microb Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24054795 Review.
References
-
- Freitas T.A.K., Saito J.A., Wan X., Hou S., Alam M. Protoglobin and globin-coupled sensors. Smallest Biomol Diatomics Interact Heme Proteins. 2008;175–202 doi: 10.1016/B978-044452839-1.50008-5. - DOI
-
- Freitas T.A.K., Hou S., Alam M. The diversity of globin-coupled sensors. FEBS Lett. 2003;552:99–104. - PubMed
-
- Hou S. A globin-coupled oxygen sensor from the facultatively alkaliphilic Bacillus halodurans C-125. Extremophiles. 2001;5:351–354. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
