Multiblock metabolomics: An approach to elucidate whole-body metabolism with multiblock principal component analysis
- PMID: 33995897
- PMCID: PMC8086023
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.04.015
Multiblock metabolomics: An approach to elucidate whole-body metabolism with multiblock principal component analysis
Abstract
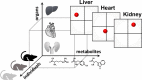
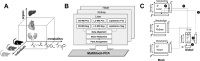
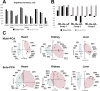
Principal component analysis (PCA) is a useful tool for omics analysis to identify underlying factors and visualize relationships between biomarkers. However, this approach is limited in addressing life complexity and further improvement is required. This study aimed to develop a new approach that combines mass spectrometry-based metabolomics with multiblock PCA to elucidate the whole-body global metabolic network, thereby generating comparable metabolite maps to clarify the metabolic relationships among several organs. To evaluate the newly developed method, Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rats (n = 6) were used as type 2 diabetic models and Sprague Dawley (SD) rats (n = 6) as controls. Metabolites in the heart, kidney, and liver were analyzed by capillary electrophoresis and liquid chromatography mass spectrometry, respectively, and the detected metabolites were analyzed by multiblock PCA. More than 300 metabolites were detected in the heart, kidney, and liver. When the metabolites obtained from the three organs were analyzed with multiblock PCA, the score and loading maps obtained were highly synchronized and their metabolism patterns were visually comparable. A significant finding in this study was the different expression patterns in lipid metabolism among the three organs; notably triacylglycerols with polyunsaturated fatty acids or less unsaturated fatty acids showed specific accumulation patterns depending on the organs.
Keywords: AMP, adenosine monophosphate; Biomarkers; CE/MS, capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry; CV, coefficient of variation; ESI, electrospray ionization; FABP, fatty acid-binding protein; GC/MS, gas chromatography mass spectrometry; LC/MS, liquid chromatography mass spectrometry; Mass spectrometry; Metabolomics; Multiblock PCA; PCA, principal component analysis; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; QC, quality control; SD, Sprague Dawley; TCA, tricarboxylic acid. CoA, coenzyme A; TG, triacylglycerol; Type 2 Diabetes; UPLC, ultra-performance liquid chromatography; ZDF, Zucker diabetic fatty.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Hocher B. Adamski J Metabolomics for clinical use and research in chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017;13:269–284. - PubMed
-
- Tyagi R., Rana P., Gupta M., Khan A.R., Bhatnagar D. Differential biochemical response of rat kidney towards low and high doses of NiCl2 as revealed by NMR spectroscopy. J Appl Toxicol. 2013;33:134–141. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
