Iranian Brain Imaging Database: A Neuropsychiatric Database of Healthy Brain
- PMID: 33995934
- PMCID: PMC8114860
- DOI: 10.32598/bcn.12.1.1774.2
Iranian Brain Imaging Database: A Neuropsychiatric Database of Healthy Brain
Abstract
Introduction: The Iranian Brain Imaging Database (IBID) was initiated in 2017, with 5 major goals: provide researchers easy access to a neuroimaging database, provide normative quantitative measures of the brain for clinical research purposes, study the aging profile of the brain, examine the association of brain structure and function, and join the ENIGMA consortium. Many prestigious databases with similar goals are available. However, they were not done on an Iranian population, and the battery of their tests (e.g. cognitive tests) is selected based on their specific questions and needs.
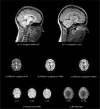
Methods: The IBID will include 300 participants (50% female) in the age range of 20 to 70 years old, with an equal number of participants (#60) in each age decade. It comprises a battery of cognitive, lifestyle, medical, and mental health tests, in addition to several Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) protocols. Each participant completes the assessments on two referral days.
Results: The study currently has a cross-sectional design, but longitudinal assessments are considered for the future phases of the study. Here, details of the methodology and the initial results of assessing the first 152 participants of the study are provided.
Conclusion: IBID is established to enable research into human brain function, to aid clinicians in disease diagnosis research, and also to unite the Iranian researchers with interests in the brain.
Keywords: Cognitive tests; Database; Healthy population; Magnetic resonance imaging.
Copyright© 2021 Iranian Neuroscience Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Åberg M. A. I., Pedersen N. L., Torén K., Svartengren M., Bäckstrand B., Johnsson T., et al. (2009). Cardiovascular fitness is associated with cognition in young adulthood. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 106(49), 20906–11. [DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0905307106] [PMID ] [PMCID ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abou-Mrad F. K. (2017). Normative data for the montreal cognitive assessment in a lebanese normative elderly population. Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association, 13(7), P1140. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2017.06.1663] - DOI
-
- Ardakani A., Seghatoleslam T., Habil H., Jameei F., Rashid R., Zahirodin A., et al. (2016). Construct validity of symptom checklist-90-revised (SCL-90-R) and general health questionnaire-28 (GHQ-28) in patients with drug addiction and diabetes, and normal population. Iranian Journal of Public Health, 45(4), 451–9. [PMCID ] [PMID ] - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous