The protective effect of Azadirachta indica (neem) against metabolic syndrome: A review
- PMID: 33995939
- PMCID: PMC8087850
- DOI: 10.22038/ijbms.2021.48965.11218
The protective effect of Azadirachta indica (neem) against metabolic syndrome: A review
Abstract
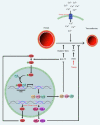
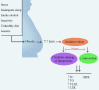
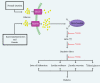
Metabolic syndrome is a condition associated with obesity, diabetes, dyslipidemia, and high blood pressure. Recently, the use of phytochemicals is suggested in the control and treatment of metabolic syndrome. The Azadirachta indica (neem) is an evergreen tree belonging to the family of Meliaceae. Multiple studies have been confirmed the anti-diabetic and anti-hypertension, anti-hyperlipidemia, and anti-obesity effects of neem. In this review, we reported the protective effects of neem against the complications of metabolic syndrome with a special focus on mechanisms that are involved. It has been shown that neem can control hyperglycemia and hypertension through over-expression of transcription factor nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and anti-oxidant effects. Neem also reduced the glucose uptake through up-regulation of glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) and inhibition of key intestinal enzymes such as glucosidases. Moreover, neem showed anti-hypertensive effects possibility via the block of calcium channels, up-regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), and extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2) signaling pathway. Anti-oxidant effects play an important role in protective mechanisms of neem against metabolic syndrome and its complications.
Keywords: Azadirachta indica; Diabetes; Hyperlipidemia; Hypertension; Metabolic syndrome; Neem; Obesity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aqueous Azadirachta indica (Neem) Extract Attenuates Insulin Resistance to Improve Glycemic Control and Endothelial Function in Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome.J Med Food. 2021 Nov;24(11):1135-1144. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2020.4838. Epub 2021 Sep 28. J Med Food. 2021. PMID: 34582720 Clinical Trial.
-
Potential benefits of phytochemicals from Azadirachta indica against neurological disorders.Neurochem Int. 2021 Jun;146:105023. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2021.105023. Epub 2021 Mar 20. Neurochem Int. 2021. PMID: 33753160 Review.
-
Azadirachta indica A. Juss (neem) against diabetes mellitus: a critical review on its phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2022 May 20;74(5):681-710. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgab098. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34562010 Review.
-
Azadirachta indica: A herbal panacea in dentistry - An update.Pharmacogn Rev. 2015 Jan-Jun;9(17):41-4. doi: 10.4103/0973-7847.156337. Pharmacogn Rev. 2015. PMID: 26009692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment with Azadirachta indica in diabetic pregnant rats: negative effects on maternal outcome.J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Oct 11;143(3):805-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.07.023. Epub 2012 Aug 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22921950
Cited by
-
Natural products in the treatment of diabetic foot infection.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Jan 7;30(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02255-y. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 39773682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methanol leaf extract of Azadirachta indica mitigates isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction through the modulation of oxidative stress, and PPARα and BCL2 signaling in rats.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2025 Jul-Aug;15(4):1328-1340. doi: 10.22038/ajp.2024.25277. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2025. PMID: 40656620 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic kidney disease combined with metabolic syndrome is a non-negligible risk factor.Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Jul 25;15:20420188241252309. doi: 10.1177/20420188241252309. eCollection 2024. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2024. PMID: 39071115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Antimicrobial Potential of the Neem Tree Azadirachta indica.Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 30;13:891535. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.891535. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35712721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of herbal therapeutics for the prevention and management of poxvirus infections.Arch Microbiol. 2025 Jun 25;207(8):186. doi: 10.1007/s00203-025-04367-3. Arch Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40560228 Review.
References
-
- Hu G, Lindstrom J, Jousilahti P, Peltonen M, Sjoberg L, Kaaja R, etal The increasing prevalence of metabolic syndrome among Finnish men and women over a decade. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:832–836. - PubMed
-
- Lee W-Y, Jung C-H, Park J-S, Rhee E-J, Kim S-W. Effects of smoking, alcohol, exercise, education, and family history on the metabolic syndrome as defined by the ATP III. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2005;67:70–77. - PubMed
-
- Toms TE, Panoulas VF, John H, Douglas KM, Kitas GD. Methotrexate therapy associates with reduced prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in rheumatoid arthritis patients over the age of 60-more than just an anti-inflammatory effect? A cross sectional study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11:R110. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hamilton MT, Hamilton DG, Zderic TW. Role of low energy expenditure and sitting in obesity, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes. 2007;56:2655–2667. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
