Trends in Poly Drug Use-associated Deaths based on Confirmed Analytical Toxicology Results in Tehran, Iran, in 2011-2016
- PMID: 33995956
- PMCID: PMC8080175
- DOI: 10.22122/ahj.v13i1.296
Trends in Poly Drug Use-associated Deaths based on Confirmed Analytical Toxicology Results in Tehran, Iran, in 2011-2016
Abstract
Background: Poly drug use is a public health threat causing morbidity and mortality all over the world. Combined use of licit and illicit drugs is among the possible causes of death. In this retrospective analytical study, we evaluated forensic toxicology analysis results from 2011 to 2016 in Tehran province, Iran.
Methods: All deaths related to poly drug use and referred to the Legal Medicine Organization, Tehran during the 6-year study period were evaluated. Postmortem samples were analyzed to detect alcohols, and prescription and illicit drugs using headspace gas chromatography (HSGC), high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) in a forensic toxicology laboratory. Manner of death, demographic characteristics, and different drug categories in postmortem samples were analyzed.
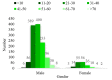
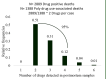
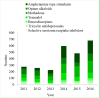
Findings: A total of 1388 poly drug use-associated deaths were investigated during the 6-year study period. Overall, victims were mostly young men of 20-40 years of age (56.8%). The male to female ratio was 7:16. Methadone (n = 660; 47.6%) and amphetamine type stimulants (ATS) (n = 657; 47.3%) were in the highest category for poly drug use-associated deaths. Moreover, in some cases, opium (n = 458; 32.9%), tramadol (n = 389; 28.0%), and tricyclic antidepressants (n = 151; 10.9%) had been used with other drugs.
Conclusion: The present study provides information about poly drug use-associated deaths in Tehran and highlights the major role of substance abuse in death.
Keywords: Amphetamine; Forensic toxicology; Methadone; Public health; Substance-related disorders.
© 2020 Kerman University of Medical Sciences.
Figures
References
-
- Auckloo M, Davies BB. Post-mortem toxicology in violent fatalities in Cape Town, South Africa: A preliminary investigation. J Forensic Leg Med. 2019;63:18–25. - PubMed
-
- Paul ABM, Simms L, Mahesan AA, Belanger EC. Teens, Drugs, and Vegas: Toxicological surveillance of illicit prescription and illegal drug abuse in adolescents (12-17 years) using post-mortem data in Clark County, Nevada from 2005 to 2015. J Forensic Leg Med. 2018;58:20–4. - PubMed
-
- Rigg KK, Sharp A. Nonmedical prescription drug use among African Americans who use MDMA (ecstasy/molly): Implications for risk reduction. Addict Behav. 2018;79:159–65. - PubMed
-
- Akhgari M, Kahfi MS, Akha HS. Analysis of intoxication deaths: Causes and manners of death. ndian J Pharm Sci. 2019;81(1):32–8.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
