Role of Flt4 in Skin Protection against UVB Radiation: A System Biology Approach
- PMID: 33995966
- PMCID: PMC7956040
- DOI: 10.34172/jlms.2020.S5
Role of Flt4 in Skin Protection against UVB Radiation: A System Biology Approach
Abstract
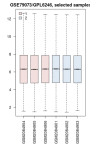
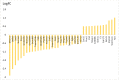
Background: Although the application of ultraviolet B (UVB) in phototherapy of human skin is a common therapeutic method, it is known as a risk factor for skin cancer. This study aims to assess the role of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) to find the critical one that is mainly responsible for skin protection against UVB radiation. Methods: The gene expression profiles of irradiated mice by UVB that issued skin protection against exposure are extracted from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and analyzed by GEO2R. The significant DEGs are assessed via gene ontology (GO) analysis and the critical individuals are investigated via action mapping. Results: Thirty-eight significant DEGs that provide skin resistance against UVB irradiation were determined. Among the query DEGs, 26 individuals were related to 43 biological terms. Flt4, F3, Tspan6, Cblb, and Itgb6 were highlighted as the critical DEGs to promote skin protection against UVB irradiation. Conclusion: The finding indicates that Flt4 is the key DEG that is mainly responsible for protecting skin from UVB exposure.
Keywords: Flt4; Gene ontology; Mouse; Skin; UVB.
Copyright © 2020 J Lasers Med Sci.
References
-
- Ramsay DL, Lish KM, Yalowitz CB, Soter NA. Ultraviolet-B phototherapy for early-stage cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Arch Dermatol. 1992;128(7):931–3. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous