Terahertz pulses induce segment renewal via cell proliferation and differentiation overriding the endogenous regeneration program of the earthworm Eisenia andrei
- PMID: 33996209
- PMCID: PMC8086446
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.416158
Terahertz pulses induce segment renewal via cell proliferation and differentiation overriding the endogenous regeneration program of the earthworm Eisenia andrei
Abstract
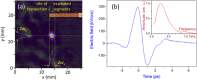
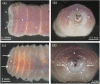
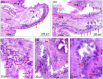
Terahertz (THz) irradiation of excised Eisenia andrei earthworms is shown to cause overriding of the genetically determined, endogenously mediated segment renewing capacity of the model animal. Single-cycle THz pulses of 5 µJ energy, 0.30 THz mean frequency, 293 kV/cm peak electric field, and 1 kHz repetition rate stimulated the cell proliferation (indicated by the high number of mitotic cells) and both histogenesis and organogenesis, producing a significantly higher number of regenerated segments. The most conspicuous alteration in THz-treated animals was the more intense development of the new central nervous system and blood vessels. These results clearly demonstrate that THz pulses are capable to efficiently trigger biological processes and suggest potential applications in medicine.
© 2021 Optical Society of America under the terms of the OSA Open Access Publishing Agreement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Intense THz Pulses with large ponderomotive potential generated from large aperture photoconductive antennas.Opt Express. 2016 May 30;24(11):11299-311. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.011299. Opt Express. 2016. PMID: 27410061
-
Enabling high repetition rate nonlinear THz science with a kilowatt-class sub-100 fs laser source.Opt Express. 2020 May 25;28(11):16951-16967. doi: 10.1364/OE.389653. Opt Express. 2020. PMID: 32549507
-
Impulsive terahertz radiation with high electric fields from an amplifier-driven large-area photoconductive antenna.Opt Express. 2010 Apr 26;18(9):9251-7. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.009251. Opt Express. 2010. PMID: 20588772
-
High-field THz pulses from a GaAs photoconductive emitter for non-linear THz studies.Opt Express. 2021 Jun 21;29(13):19920-19927. doi: 10.1364/OE.427247. Opt Express. 2021. PMID: 34266092
-
Powerful terahertz waves from long-wavelength infrared laser filaments.Light Sci Appl. 2020 Nov 12;9(1):186. doi: 10.1038/s41377-020-00423-3. Light Sci Appl. 2020. PMID: 33298833 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Terahertz exposure enhances neuronal synaptic transmission and oligodendrocyte differentiation in vitro.iScience. 2021 Nov 22;24(12):103485. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103485. eCollection 2021 Dec 17. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34927027 Free PMC article.
-
The biological effects of terahertz wave radiation-induced injury on neural stem cells.iScience. 2023 Jul 18;26(10):107418. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107418. eCollection 2023 Oct 20. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37771661 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous wave irradiation at 0.1 terahertz facilitates transmembrane transport of small molecules.iScience. 2022 Feb 22;25(3):103966. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.103966. eCollection 2022 Mar 18. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35281735 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilmink G. J., Rivest B. D., Roth C. C., Ibey B. L., Payne J. A., Cundin L. X., Grundt J. E., Peralta X., Mixon D. G., Roach W. P., “In vitro investigation of the biological effects associated with human dermal fibroblasts exposed to 2.52 THz radiation,” Lasers Surg. Med. 43(2), 152–163 (2011).10.1002/lsm.20960 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wilmink G. J., Rivest B. D., Ibey B. L., Roth C. L., Bernhard J., Roach W. P., “Quantitative investigation of the bioeffects associated with terahertz radiation,” Opt. Interact. with Tissues Cells XXI 7562, 75620L (2010).
-
- Olshevskaya J. S., Ratushnyak A. S., Petrov A. K., Kozlov A. S., Zapara T. A., “Effect of terahertz electromagnetic waves on neurons systems,” Int. Conf. Comput. Technol. Electr. Electron. Eng. 210–211 (2008).10.1109/SIBIRCON.2008.4602607 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
