Therapeutic Dilemmas Regarding Anticoagulation, Pulmonary Embolism, and Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage Due to Behçet's Disease
- PMID: 33996295
- PMCID: PMC8114959
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.14429
Therapeutic Dilemmas Regarding Anticoagulation, Pulmonary Embolism, and Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage Due to Behçet's Disease
Abstract
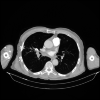
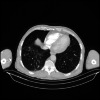
The use of anticoagulants is still a matter of debate in deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and other thrombotic events in Behcet's disease (BD). Anticoagulant therapy is an integral part of treatment in cases of a pulmonary embolism (PE) that develops in other disorders. The issue of how to act when a pulmonary artery thrombosis is reported in the Behçet's patient may pose a major dilemma among emergency physicians. A 61-year-old male came to our ED with a complaint of chest pain and hemoptysis. The patient had tachypnea, dyspnea, tachycardia, a decrease of breath sounds in the basal regions of both lungs, and a few crackling rales were heard in the left lung field. Chest CT angiography showed pulmonary thromboembolism in the right middle and lower lobe segment arteries with pulmonary infarction as well as ground glass densities compatible with alveolar hemorrhage. High-dose steroid and cyclophosphamide were administered immediately without anticoagulant therapy based on pulmonary vasculitis and de novo clot formation in the pulmonary circulation. Clinical improvement was observed after four days of admission. The patient remained under observation with oral prednisolone and cyclophosphamide monthly. PE is almost non-existent in patients with BD, and signs of pulmonary artery thrombosis are associated with pulmonary vasculitis. Delaying immunosuppressive therapy may result in unwanted results in these kinds of patients. This case underlines the importance of recognizing this manifestation early to prevent potentially fatal consequences.
Keywords: alveolar hemorrhage; behçet’s disease; pulmonary thromboembolism.
Copyright © 2021, Ahmadzai et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Consider Behcet's disease in young patients with deep vein thrombosis.Respir Med Case Rep. 2016 Apr 14;18:41-4. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2016.04.002. eCollection 2016. Respir Med Case Rep. 2016. PMID: 27144118 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical lung biopsy to diagnose Behcet's vasculitis with adult respiratory distress syndrome.Lung India. 2014 Oct;31(4):387-9. doi: 10.4103/0970-2113.142127. Lung India. 2014. PMID: 25378849 Free PMC article.
-
A rare but serious manifestation of Behçet's disease: intracardiac thrombus in 22 patients.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014 Jul-Aug;32(4 Suppl 84):S87-92. Epub 2014 Jul 28. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 25068833
-
Pulmonary manifestations in Behçet's syndrome.Chest. 1989 Mar;95(3):585-9. doi: 10.1378/chest.95.3.585. Chest. 1989. PMID: 2646075 Review.
-
Behçet's Disease: A Radiological Review of Vascular and Parenchymal Pulmonary Involvement.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Nov 19;12(11):2868. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12112868. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428928 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical characteristics and risk factors predictive of pulmonary embolism complicated in bronchiectasis patients: a retrospective study.BMC Pulm Med. 2022 Jun 9;22(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-02016-9. BMC Pulm Med. 2022. PMID: 35681174 Free PMC article.
-
Aseptic Abscess of the Spleen as an Antecedent Manifestation of Behçet's Disease.Cureus. 2023 May 1;15(5):e38375. doi: 10.7759/cureus.38375. eCollection 2023 May. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37265896 Free PMC article.
-
Computed tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA) in Behçet's disease patients: a remarkable gender gap and time to refine the treatment strategy.Clin Rheumatol. 2022 Jan;41(1):195-201. doi: 10.1007/s10067-021-05991-2. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Clin Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 34767109
References
-
- Pulmonary artery aneurysms in Behçet syndrome. Hamuryudan V, Er T, Seyahi E, et al. Am J Med. 2004;117:867–870. - PubMed
-
- Pulmonary artery involvement and associated lung disease in Behçet disease: a series of 47 patients. Seyahi E, Melikoglu M, Akman C, et al. Medicine (Baltimore) 2012;91:35–48. - PubMed
-
- Nephrotic syndrome. Wang C-S, Greenbaum LA. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2019;66:73–85. - PubMed
-
- Multiple pulmonary arterial aneurysms in Behçet's disease and Hughes-Stovin syndrome. Durieux P, Bletry O, Huchon G, Wechsler B, Chretien J, Godeau P. Am J Med. 1981;71:736–741. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources