Recent advances in drug delivery applications of cubosomes, hexosomes, and solid lipid nanoparticles
- PMID: 33996404
- PMCID: PMC8105777
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.02.013
Recent advances in drug delivery applications of cubosomes, hexosomes, and solid lipid nanoparticles
Abstract
The use of lipid nanocarriers for drug delivery applications is an active research area, and a great interest has particularly been shown in the past two decades. Among different lipid nanocarriers, ISAsomes (Internally self-assembled somes or particles), including cubosomes and hexosomes, and solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) have unique structural features, making them attractive as nanocarriers for drug delivery. In this contribution, we focus exclusively on recent advances in formation and characterization of ISAsomes, mainly cubosomes and hexosomes, and their use as versatile nanocarriers for different drug delivery applications. Additionally, the advantages of SLNs and their application in oral and pulmonary drug delivery are discussed with focus on the biological fates of these lipid nanocarriers in vivo. Despite the demonstrated advantages in in vitro and in vivo evaluations including preclinical studies, further investigations on improved understanding of the interactions of these nanoparticles with biological fluids and tissues of the target sites is necessary for efficient designing of drug nanocarriers and exploring potential clinical applications.
Keywords: Biological fate; Cubosomes; Drug delivery; Hexosomes; Inverse non-lamellar liquid crystalline phases; Nano-self-assemblies; Solid crystalline phases; Solid lipid nanoparticles.
© 2021 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

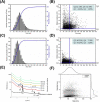
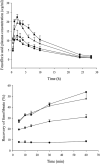
 ), 400 nm LMPs (
), 400 nm LMPs ( ), microparticles (
), microparticles ( ) and control (
) and control ( ) in male Wistar rats (fenofibrate dosed at 12.5 mg/animal, n = 6, mean ± SEM). (B) Recovery of fenofibrate (%) in the aqueous phase (mean ± SEM) during in vitro lipolysis of 100 nm SLN (
) in male Wistar rats (fenofibrate dosed at 12.5 mg/animal, n = 6, mean ± SEM). (B) Recovery of fenofibrate (%) in the aqueous phase (mean ± SEM) during in vitro lipolysis of 100 nm SLN ( ), 400 nm SLN (
), 400 nm SLN ( ), microparticles (
), microparticles ( ) and control (
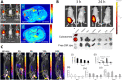
) and control ( ) (n = 3 except 100 nm, 60 min is n = 1 (SEM not shown) and 400 nm, 60 min is n = 2). Modified with permission from Ref. .
) (n = 3 except 100 nm, 60 min is n = 1 (SEM not shown) and 400 nm, 60 min is n = 2). Modified with permission from Ref. .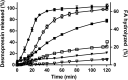
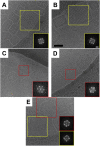
 , TG14 particles;
, TG14 particles;  , TG16 particles;
, TG16 particles;  , TG18 particles. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3). Reproduced with permission from Ref. .
, TG18 particles. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3). Reproduced with permission from Ref. .
References
-
- Couvreur P., Vauthier C. Nanotechnology: intelligent design to treat complex disease. Pharm Res (N Y) 2006;23:1417–1450. - PubMed
-
- Moghimi S.M., Hunter A.C., Murray J.C. Nanomedicine: current status and future prospects. Faseb J. 2005;19:311–330. - PubMed
-
- Wibroe P.P., Ahmadvand D., Oghabian M.A., Yaghmur A., Moghimi S.M. An integrated assessment of morphology, size, and complement activation of the PEGylated liposomal doxorubicin products Doxil®, Caelyx®, DOXOrubicin, and SinaDoxosome. J Control Release. 2016;221:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Bor G., Mat Azmi I.D., Yaghmur A. Nanomedicines for cancer therapy: current status, challenges and future prospects. Ther Deliv. 2019;10:113–132. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

