Surgical treatment of metastatic germ cell cancer
- PMID: 33996470
- PMCID: PMC8099653
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajur.2020.05.007
Surgical treatment of metastatic germ cell cancer
Abstract
Among young men between the ages of 15 and 40 years, germ cell cancer is the most common solid tumor [1]. The worldwide incidence of germ cell cancer is 70 000 cases. Compared to all solid tumors of men, germ cell cancer accounts for 1% of all male tumors. Nevertheless, the mortality of this rare tumor entity is about 13% since 9507 patients died worldwide of germ cell cancer. The improvement in survival of germ cell cancer patients is due to a multimodal treatment of germ cell cancer including cisplatin-based chemotherapy and surgery leading to higher cure-rates even in advanced stages [1], whereas the increasing incidence of germ cell cancers cannot be thoroughly explained. In this article we review the current indications for surgery in metastatic germ cell cancers, highlight the strength and weaknesses of techniques and indications and raise the question how to improve surgical treatment in metastatic germ cell cancer.
Keywords: Germ cell cancer; Metastatic germ cell cancer; Retroperitoneal lymphnode dissection; Retroperitoneal surgery.
© 2021 Editorial Office of Asian Journal of Urology. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
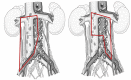
Figures
References
-
- Albers P., Albrecht W., Algaba F., Bokemeyer C., Cohn-Cedermark G., Fizazi K. Guidelines on testicular cancer: 2015 update. Eur Urol. 2015;68:1054–1068. - PubMed
-
- These; Paris: 1906. C M. Tumeurs du testicule.
-
- International germ cell consensus classification: a prognostic factor-based staging system for metastatic germ cell cancers. International Germ Cell Cancer Collaborative Group. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15:594–603. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

