Individualized Prediction of Colorectal Cancer Metastasis Using a Radiogenomics Approach
- PMID: 33996544
- PMCID: PMC8113949
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.620945
Individualized Prediction of Colorectal Cancer Metastasis Using a Radiogenomics Approach
Abstract
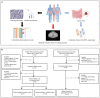
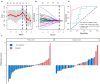
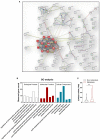
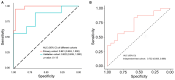
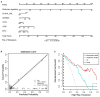
Objectives: To evaluate whether incorporating the radiomics, genomics, and clinical features allows prediction of metastasis in colorectal cancer (CRC) and to develop a preoperative nomogram for predicting metastasis. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed radiomics features of computed tomography (CT) images in 134 patients (62 in the primary cohort, 28 in the validation cohort, and 44 in the independent-test cohort) clinicopathologically diagnosed with CRC at Dazhou Central Hospital from February 2018 to October 2019. Tumor tissues were collected from all patients for RNA sequencing, and clinical data were obtained from medical records. A total of 854 radiomics features were extracted from enhanced venous-phase CT of CRC. Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression analysis was utilized for data dimension reduction, feature screen, and radiomics signature development. Multivariable logistic regression analysis was performed to build a multiscale predicting model incorporating the radiomics, genomics, and clinical features. The receiver operating characteristic curve, calibration curve, and decision curve were conducted to evaluate the performance of the nomogram. Results: The radiomics signature based on 16 selected radiomics features showed good performance in metastasis assessment in both primary [area under the curve (AUC) = 0.945, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.892-0.998] and validation cohorts (AUC = 0.754, 95% CI 0.570-0.938). The multiscale nomogram model contained radiomics features signatures, four-gene expression related to cell cycle pathway, and CA 19-9 level. The multiscale model showed good discrimination performance in the primary cohort (AUC = 0.981, 95% CI 0.953-1.000), the validation cohort (AUC = 0.822, 95% CI 0.635-1.000), and the independent-test cohort (AUC = 0.752, 95% CI 0.608-0.896) and good calibration. Decision curve analysis confirmed the clinical application value of the multiscale model. Conclusion: This study presented a multiscale model that incorporated the radiological eigenvalues, genomics features, and CA 19-9, which could be conveniently utilized to facilitate the individualized preoperatively assessing metastasis in CRC patients.
Keywords: carbohydrate antigen 19-9; colorectal cancer; genomics; metastasis; radiomics.
Copyright © 2021 Liu, Li, Xu, Wang, Zeng, Fu, Huang, Chu, Wang, Zhang and Zeng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

