Doxycycline Induces Apoptosis of Brucella Suis S2 Strain-Infected HMC3 Microglial Cells by Activating Calreticulin-Dependent JNK/p53 Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 33996626
- PMCID: PMC8113685
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.640847
Doxycycline Induces Apoptosis of Brucella Suis S2 Strain-Infected HMC3 Microglial Cells by Activating Calreticulin-Dependent JNK/p53 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
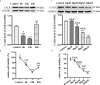
Neurobrucellosis is a chronic complication of human brucellosis that is caused by the presence of Brucella spp in the central nervous system (CNS) and the inflammation play a key role on the pathogenesis. Doxycycline (Dox) is a widely used antibiotic that induces apoptosis of bacteria-infected cells. However, the mechanisms of Brucella inhibition of microglial apoptosis and Dox induction of apoptosis are still poorly understood. In this study, we found that Brucella suis S2 strain (B. suis S2) increased calreticulin (CALR) protein levels and inhbited HMC3 cell apoptosis. Hence, we constructed two HMC3 cell line variants, one with stable overexpression (HMC3-CALR) and one with low expression of CALR (HMC3-sh-CALR). CALR was found to decrease levels of p-JNK and p-p53 proteins, as well as suppress apoptosis in HMC3 cells. These findings suggest that CALR suppresses apoptosis by inhibiting the JNK/p53 signaling pathway. Next, we treated HMC3, HMC3-CALR and HMC3-sh-CALR cell lines with B. suis S2 or Dox. Our results demonstrate that B. suis S2 restrains the JNK/p53 signaling pathway to inhibit HMC3 cell apoptosis via increasing CALR protein expression, while Dox plays the opposite role. Finally, we treated B. suis S2-infected HMC3 cells with Dox. Our results confirm that Dox induces JNK/p53-dependent apoptosis in B. suis S2-infected HMC3 cells through inhibition of CALR protein expression. Taken together, these results reveal that CALR and the JNK/p53 signaling pathway may serve as novel therapeutic targets for treatment of neurobrucellosis.
Keywords: Brucella suis S2 strain; JNK/p53 signaling pathway; apoptosis; doxycycline; human microglia; neurobrucellosis.
Copyright © 2021 Wang, Wang, Yang, Guo and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Brucella suis S2 strain inhibits IRE1/caspase-12/caspase-3 pathway-mediated apoptosis of microglia HMC3 by affecting the ubiquitination of CALR.mSphere. 2025 Mar 25;10(3):e0094124. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00941-24. Epub 2025 Feb 28. mSphere. 2025. PMID: 40019270 Free PMC article.
-
Doxycycline-Induced Apoptosis in Brucella suis S2-Infected HMC3 Cells via Calreticulin Suppression and Activation of the IRE1/Caspase-3 Signaling Pathway.Infect Drug Resist. 2025 Apr 23;18:2005-2020. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S507193. eCollection 2025. Infect Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 40290405 Free PMC article.
-
Brucella suis Vaccine Strain 2 Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress that Affects Intracellular Replication in Goat Trophoblast Cells In vitro.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016 Feb 9;6:19. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00019. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26904517 Free PMC article.
-
The innate immune response against Brucella in humans.Vet Microbiol. 2002 Dec 20;90(1-4):383-94. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(02)00223-7. Vet Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12414158 Review.
-
Boar hunting and brucellosis caused by Brucella suis.Travel Med Infect Dis. 2017 Mar-Apr;16:18-22. doi: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2017.03.006. Epub 2017 Mar 12. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28300645 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell and Tissue Tropism of Brucella spp.Infect Immun. 2023 May 16;91(5):e0006223. doi: 10.1128/iai.00062-23. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Infect Immun. 2023. PMID: 37129522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brucella suis S2 strain inhibits IRE1/caspase-12/caspase-3 pathway-mediated apoptosis of microglia HMC3 by affecting the ubiquitination of CALR.mSphere. 2025 Mar 25;10(3):e0094124. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00941-24. Epub 2025 Feb 28. mSphere. 2025. PMID: 40019270 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond survival to domination: Brucella's multilayered strategies for evading host immune responses.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jun 18;16:1608617. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1608617. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40606156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Downregulation of Three Novel miRNAs in the Lymph Nodes of Sheep Immunized With the Brucella suis Strain 2 Vaccine.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Feb 22;9:813170. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.813170. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35274021 Free PMC article.
-
Doxycycline-Induced Apoptosis in Brucella suis S2-Infected HMC3 Cells via Calreticulin Suppression and Activation of the IRE1/Caspase-3 Signaling Pathway.Infect Drug Resist. 2025 Apr 23;18:2005-2020. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S507193. eCollection 2025. Infect Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 40290405 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

