Normalization of B Cell Subsets but Not T Follicular Helper Phenotypes in Infants With Very Early Antiretroviral Treatment
- PMID: 33996678
- PMCID: PMC8118125
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2021.618191
Normalization of B Cell Subsets but Not T Follicular Helper Phenotypes in Infants With Very Early Antiretroviral Treatment
Abstract
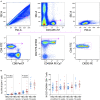
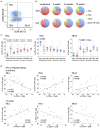
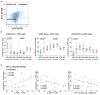
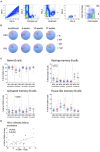
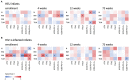
Introduction: Infant HIV-1-infection is associated with high morbidity and mortality if antiretroviral treatment (ART) is not initiated promptly. We characterized development of circulating T follicular helper cells (cTfh) and their relationship to naïve/memory B cell subsets in a cohort of neonates initiating ART within the first week of life. Methods: Infants were diagnosed within 48 hours of birth and started ART as soon as possible. The frequency and phenotype of cTfh and B cells were analyzed at enrollment (birth -19 days) and at 4, 12, and 72 weeks of age in blood of 27 HIV-1-intrauterine-infected and 25 HIV-1 exposed uninfected (HEU) infants as part of a study in Johannesburg, South Africa. cTfh cells were divided into Tfh1, Tfh2, and Tfh17 subsets. B cell phenotypes were defined as naïve, resting memory, activated memory and tissue-like memory cells. Results: HIV-1-infected infants had higher frequencies of cTfh cells than HEU infants up to 12 weeks of age and these cTfh cells were polarized toward the Tfh1 subset. Higher frequencies of Tfh1 and lower frequencies of Tfh2 and Tfh17 correlated with lower CD4+ T cell percentages. Lower frequencies of resting memory, with corresponding higher frequencies of activated memory B cells, were observed with HIV-1 infection. Importantly, dysregulations in B cell, but not cTfh cell, subsets were normalized by 72 weeks. Conclusion: Very early ART initiation in HIV-1-infected infants normalizes B cell subsets but does not fully normalize perturbations in cTfh cell subsets which remain Tfh1 polarized at 72 weeks. It remains to be determined if very early ART improves vaccine antibody responses despite the cTfh and B cell perturbations observed over the time course of this study.
Keywords: B cells; HIV-1; cTfh; early antiretroviral therapy; infants.
Copyright © 2021 Shalekoff, Loubser, Dias, Strehlau, Shiau, Wang, He, Abrams, Kuhn and Tiemessen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tagarro A, Chan M, Zangari P, Ferns B, Foster C, De Rossi A, et al. Early and highly suppressive antiretroviral therapy are main factors associated with low viral reservoir in European perinatally HIV-infected children. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. (2018) 79:269–76. 10.1097/QAI.0000000000001789 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

