A Bifunctional Nanosilver-Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite for Label-Free Electrochemical Immunosensing
- PMID: 33996742
- PMCID: PMC8113703
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2021.631571
A Bifunctional Nanosilver-Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite for Label-Free Electrochemical Immunosensing
Abstract
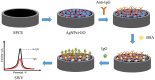
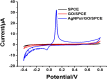
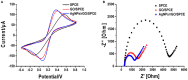
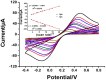
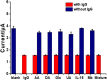
A bi-functional material based on silver nanoparticles (AgNPs)-reduced graphene oxide (rGO) composite for both electrode modification and signal generation is successfully synthesized for use in the construction of a label-free electrochemical immunosensor. An AgNPs/rGO nanocomposite is prepared by a one-pot wet chemical process. The AgNPs/rGO composite dispersion is simply cast on a screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE) to fabricate the electrochemical immunosensor. It possesses a sufficient conductivity/electroreactivity and improves the electrode reactivity of SPCE. Moreover, the material can generate an analytical response due to the formation of immunocomplexes for detection of human immunoglobulin G (IgG), a model biomarker. Based on electrochemical stripping of AgNPs, the material reveals signal amplification without external redox molecules/probes. Under optimized conditions, the square wave voltammetric peak current is responded to the logarithm of IgG concentration in two wide linear ranges from 1 to 50 pg.ml-1 and 0.05 to 50 ng.ml-1, and the limit of detection (LOD) is estimated to be 0.86 pg.ml-1. The proposed immunosensor displays satisfactory sensitivity and selectivity. Importantly, detection of IgG in human serum using the immunosensor shows satisfactory accuracy, suggesting that the immunosensor possesses a huge potential for further development in clinical diagnosis.
Keywords: Immunoglobulin G; electrochemistry; immunosensor; reduced graphene oxide; screen-printed carbon electrode; silver nanoparticles.
Copyright © 2021 Chanarsa, Jakmunee and Ounnunkad.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Awan M., Rauf S., Abbas A., Nawaz M. H., Yang C., Shahid S. A., et al. (2020). A sandwich electrochemical immunosensor based on antibody functionalized-silver nanoparticles (Ab-Ag NPs) for the detection of dengue biomarker protein NS1. J. Mol. Liq. 317:114014. 10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114014 - DOI
-
- Barman S. C., Zahed M. A., Sharifuzzaman M., Ko S. G., Yoon H., Nah J. S., et al. (2020). A polyallylamine anchored amine-rich laser-ablated graphene platform for facile and highly selective electrochemical IgG biomarker detection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30:1907297. 10.1002/adfm.201907297 - DOI
-
- Chaiyo S., Mehmeti E., Žagar K., Siangproh W., Chailapakul O., Kalcher K. (2016). Electrochemical sensors for the simultaneous determination of zinc, cadmium and lead using a Nafion/ionic liquid/graphene composite modified screen-printed carbon electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta. 918, 26–34. 10.1016/j.aca.2016.03.026 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chanarsa S., Pothipor C., Kungwan N., Ounnunkad K. (2020). A poly(pyrrole-3-carboxylic acid) thin film modified screen printed carbon electrode as highly sensitive and selective label-free electrochemical immunosensing platform. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 47, 530–541.
-
- Chen S., Yang Y., Li W., Song Y., Shi L. (2020). A sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor using Ag@CeO2-Au as a lable for sensitive detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Microchem. J. 159:105415. 10.1016/j.microc.2020.105415 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

