Metal-Free Direct C-H Functionalization of Quinoxalin-2(1 H)-Ones to Produce 3-Vinylated Quinoxalin-2(1 H)-Ones in the Presence of Alkenes
- PMID: 33996765
- PMCID: PMC8119786
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2021.672051
Metal-Free Direct C-H Functionalization of Quinoxalin-2(1 H)-Ones to Produce 3-Vinylated Quinoxalin-2(1 H)-Ones in the Presence of Alkenes
Abstract
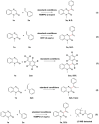
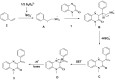
A novel and efficient C 3-H vinylation reaction with quinoxalin-2(1H)-one as the substrate, in the presence of alkenes, under metal-free conditions, is reported herein. The reaction leads to the formation of new carbon-carbon bonds that exhibit moderate to good reactivities. The vinylation of quinoxalin-2(1H)-ones, in the presence of alkenes, is an attractive process that can be potentially utilized to produce biologically active 3-vinylated quinoxalin-2(1H)-ones.
Keywords: C–H functionalization; alkenes; ammonium persulfate; cross-dehydrocoupling; vinylation.
Copyright © 2021 Ding, Li, Chang, Liu, Yu, Lv and Hu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bag S., Maiti D. (2016). Palladium-catalyzed olefination of aryl C–H bonds by using directing scaffolds. Synthesis 48, 804–815. 10.1055/s-0035-1561321 - DOI
-
- Fu J., Yuan J., Zhang Y., Xiao Y., Mao P., Diao X., et al. (2018). Copper-catalyzed oxidative coupling of quinoxalin-2(1H)-ones with alcohols: access to hydroxyalkylation of quinoxalin-2(1H)-ones. Org. Chem. Front. 5, 3382–3390. 10.1039/C8QO00979A - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

