Ubiquinone Binding and Reduction by Complex I-Open Questions and Mechanistic Implications
- PMID: 33996767
- PMCID: PMC8119997
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2021.672851
Ubiquinone Binding and Reduction by Complex I-Open Questions and Mechanistic Implications
Abstract
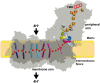
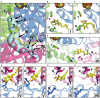
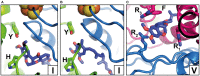
NADH: ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I) is the first enzyme complex of the respiratory chain. Complex I is a redox-driven proton pump that contributes to the proton motive force that drives ATP synthase. The structure of complex I has been analyzed by x-ray crystallography and electron cryo-microscopy and is now well-described. The ubiquinone (Q) reduction site of complex I is buried in the peripheral arm and a tunnel-like structure is thought to provide access for the hydrophobic substrate from the membrane. Several intermediate binding positions for Q in the tunnel were identified in molecular simulations. Structural data showed the binding of native Q molecules and short chain analogs and inhibitors in the access pathway and in the Q reduction site, respectively. We here review the current knowledge on the interaction of complex I with Q and discuss recent hypothetical models for the coupling mechanism.
Keywords: NADH dehydrogenase; electron transfer; inhibitor; oxidative phosphorylation; proton pumping; respiratory chain; semiquinone.
Copyright © 2021 Galemou Yoga, Schiller and Zickermann.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

