Nitric Oxide Alleviated High Salt-Induced Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis and Autophagy Independent of Blood Pressure in Rats
- PMID: 33996809
- PMCID: PMC8117152
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.646575
Nitric Oxide Alleviated High Salt-Induced Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis and Autophagy Independent of Blood Pressure in Rats
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Nitric oxide alleviated high salt-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and autophagy independent of blood pressure in rats.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jul 25;12:1419893. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1419893. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39119038 Free PMC article.
Abstract
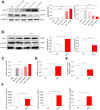
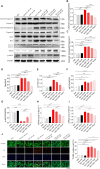
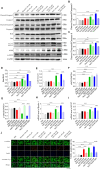
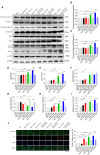
The present study aimed to explore whether high-salt diet (HSD) could cause cardiac damage independent of blood pressure, and whether nitric oxide (NO) could alleviate high-salt-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and autophagy in rats. The rats received 8% HSD in vivo. H9C2 cells or primary neonatal rat cardiomyocytes (NRCM) were treated with sodium chloride (NaCl) in vitro. The levels of cleaved-caspase 3/caspase 3, cleaved-caspase 8/caspase 8, Bax/Bcl2, LC3 II/LC3 I, Beclin-1 and autophagy related 7 (ATG7) were increased in the heart of HSD rats with hypertension (HTN), and in hypertension-prone (HP) and hypertension-resistant (HR) rats. Middle and high doses (50 and 100 mM) of NaCl increased the level of cleaved-caspase 3/caspase 3, cleaved-caspase 8/caspase 8, Bax/Bcl2, LC3 II/LC3 I, Beclin-1, and ATG7 in H9C2 cells and NRCM. The endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) level was increased, but p-eNOS level was reduced in the heart of HSD rats and H9C2 cells treated with 100 mM NaCl. The level of NO was reduced in the serum and heart of HSD rats. NO donor sodium nitroprusside (SNP) reversed the increases of cleaved-caspase 3/caspase 3, cleaved-caspase 8/caspase 8, Bax/Bcl2 induced by NaCl (100 mM) in H9C2 cells and NRCM. SNP treatment attenuated the increases of cleaved-caspase 3/caspase 3, Bax/Bcl2, LC3 II/LC3 I, Beclin-1, and ATG7 in the heart, but had no effect on the blood pressure of HSD rats with HR. These results demonstrated that HSD enhanced cardiac damage independently of blood pressure. Exogenous NO supplementarity could alleviate the high salt-induced apoptosis and autophagy in cardiomyocytes.
Keywords: apoptosis; autophagy; cardiomyocytes; high-salt diet; nitric oxide; sodium nitroprusside.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Wu, Mao, Liu, Wu, Tang, Zhao and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Cai W., Lang M., Jiang X., Yu Q., Zhou C., Zou W., et al. (2020). Correlation among high salt intake, blood pressure variability, and target organ damage in patients with essential hypertension: Study protocol clinical trial (SPIRIT compliant). Medicine 99:e19548. 10.1097/md.0000000000019548 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

