BRCA1 and BRCA2 Tumor Suppressor Function in Meiosis
- PMID: 33996823
- PMCID: PMC8121103
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.668309
BRCA1 and BRCA2 Tumor Suppressor Function in Meiosis
Abstract
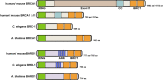
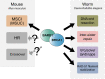
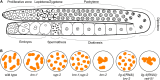
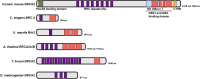
Meiosis is a specialized cell cycle that results in the production of haploid gametes for sexual reproduction. During meiosis, homologous chromosomes are connected by chiasmata, the physical manifestation of crossovers. Crossovers are formed by the repair of intentionally induced double strand breaks by homologous recombination and facilitate chromosome alignment on the meiotic spindle and proper chromosome segregation. While it is well established that the tumor suppressors BRCA1 and BRCA2 function in DNA repair and homologous recombination in somatic cells, the functions of BRCA1 and BRCA2 in meiosis have received less attention. Recent studies in both mice and the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans have provided insight into the roles of these tumor suppressors in a number of meiotic processes, revealing both conserved and organism-specific functions. BRCA1 forms an E3 ubiquitin ligase as a heterodimer with BARD1 and appears to have regulatory roles in a number of key meiotic processes. BRCA2 is a very large protein that plays an intimate role in homologous recombination. As women with no indication of cancer but carrying BRCA mutations show decreased ovarian reserve and accumulated oocyte DNA damage, studies in these systems may provide insight into why BRCA mutations impact reproductive success in addition to their established roles in cancer.
Keywords: BARD1; BRCA1; BRCA2; DSBs; MSCI; meiosis; recombination.
Copyright © 2021 Li and Engebrecht.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential requirement for BRCA1-BARD1 E3 ubiquitin ligase activity in DNA damage repair and meiosis in the Caenorhabditis elegans germ line.PLoS Genet. 2023 Jan 30;19(1):e1010457. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010457. eCollection 2023 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 36716349 Free PMC article.
-
Excess crossovers impede faithful meiotic chromosome segregation in C. elegans.PLoS Genet. 2020 Sep 4;16(9):e1009001. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009001. eCollection 2020 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32886661 Free PMC article.
-
BRCA-related ATM-mediated DNA double-strand break repair and ovarian aging.Hum Reprod Update. 2020 Jan 1;26(1):43-57. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmz043. Hum Reprod Update. 2020. PMID: 31822904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) proteins promote homolog-independent recombination repair in meiosis crucial for germ cell genomic stability.PLoS Genet. 2010 Jul 22;6(7):e1001028. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001028. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 20661436 Free PMC article.
-
Meiotic recombination: insights into its mechanisms and its role in human reproduction with a special focus on non-obstructive azoospermia.Hum Reprod Update. 2022 Nov 2;28(6):763-797. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmac024. Hum Reprod Update. 2022. PMID: 35613017 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential requirement for BRCA1-BARD1 E3 ubiquitin ligase activity in DNA damage repair and meiosis in the Caenorhabditis elegans germ line.PLoS Genet. 2023 Jan 30;19(1):e1010457. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010457. eCollection 2023 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 36716349 Free PMC article.
-
BRCA1 and Its Vulnerable C-Terminal BRCT Domain: Structure, Function, Genetic Mutations and Links to Diagnosis and Treatment of Breast and Ovarian Cancer.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Mar 4;17(3):333. doi: 10.3390/ph17030333. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38543119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Blood Serum Inhibits Ductal Carcinoma Cells BT474 Growth and Modulates Effect of HER2 Inhibition.Biomedicines. 2022 Aug 8;10(8):1914. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10081914. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36009461 Free PMC article.
-
Biallelic BRCA2 variants induce premature ovarian insufficiency by impaired meiotic homologous recombination.Commun Biol. 2025 Jul 25;8(1):1104. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-08426-9. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40715368 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria: the epigenetic regulators of ovarian aging and longevity.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Nov 13;15:1424826. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1424826. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39605943 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

