The Potential of Physical Exercise to Mitigate Radiation Damage-A Systematic Review
- PMID: 33996841
- PMCID: PMC8117229
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.585483
The Potential of Physical Exercise to Mitigate Radiation Damage-A Systematic Review
Abstract
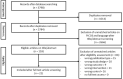
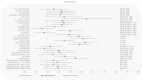
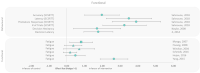
There is a need to investigate new countermeasures against the detrimental effects of ionizing radiation as deep space exploration missions are on the horizon. Objective: In this systematic review, the effects of physical exercise upon ionizing radiation-induced damage were evaluated. Methods: Systematic searches were performed in Medline, Embase, Cochrane library, and the databases from space agencies. Of 2,798 publications that were screened, 22 studies contained relevant data that were further extracted and analyzed. Risk of bias of included studies was assessed. Due to the high level of heterogeneity, meta-analysis was not performed. Five outcome groups were assessed by calculating Hedges' g effect sizes and visualized using effect size plots. Results: Exercise decreased radiation-induced DNA damage, oxidative stress, and inflammation, while increasing antioxidant activity. Although the results were highly heterogeneous, there was evidence for a beneficial effect of exercise in cellular, clinical, and functional outcomes. Conclusions: Out of 72 outcomes, 68 showed a beneficial effect of physical training when exposed to ionizing radiation. As the first study to investigate a potential protective mechanism of physical exercise against radiation effects in a systematic review, the current findings may help inform medical capabilities of human spaceflight and may also be relevant for terrestrial clinical care such as radiation oncology.
Keywords: DNA damage; deep space exploration; human spaceflight; ionizing radiation; oxidative stress; physical exercise; radiation countermeasures.
Copyright © 2021 Kim, Weber, Straube, Hellweg, Nasser, Green and Fogtman.
Conflict of interest statement
TW and DG were employed by the company KBR GmbH. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of Spaceflight on Musculoskeletal Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis, Considerations for Interplanetary Travel.Sports Med. 2021 Oct;51(10):2097-2114. doi: 10.1007/s40279-021-01496-9. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Sports Med. 2021. PMID: 34115344 Free PMC article.
-
Ionizing radiation-induced risks to the central nervous system and countermeasures in cellular and rodent models.Int J Radiat Biol. 2021;97(sup1):S132-S150. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2020.1820598. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Int J Radiat Biol. 2021. PMID: 32946305 Review.
-
Physical activity and exercise for cancer-related cognitive impairment among individuals affected by childhood cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2023 Jan;7(1):47-58. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(22)00286-3. Epub 2022 Oct 27. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2023. PMID: 36309037
-
Behavioural modification interventions for medically unexplained symptoms in primary care: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Sep;24(46):1-490. doi: 10.3310/hta24460. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32975190 Free PMC article.
-
Physiotherapy rehabilitation after total knee or hip replacement: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2005;5(8):1-91. Epub 2005 Jun 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2005. PMID: 23074477 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genomic Changes Driven by Radiation-Induced DNA Damage and Microgravity in Human Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 29;22(19):10507. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910507. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exercise Across the Phases of Cancer Survivorship: A Narrative Review.Yonsei Med J. 2024 Jun;65(6):315-323. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2023.0638. Yonsei Med J. 2024. PMID: 38804025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Function-Genes and Disease-Genes Prediction Based on Network Embedding and One-Class Classification.Interdiscip Sci. 2024 Dec;16(4):781-801. doi: 10.1007/s12539-024-00638-7. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Interdiscip Sci. 2024. PMID: 39230798
-
Exercise alleviates hematopoietic stem cell injury following radiation via the carnosine/Slc15a2-p53 axis.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Dec 3;22(1):582. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01959-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39627813 Free PMC article.
-
From Lawn to Health: Understanding the Prostate Cancer Risk in Light DIY Activities.Am J Mens Health. 2024 Sep-Oct;18(5):15579883241287386. doi: 10.1177/15579883241287386. Am J Mens Health. 2024. PMID: 39397489 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

