Development and Validation of Automated Visual Field Report Extraction Platform Using Computer Vision Tools
- PMID: 33996848
- PMCID: PMC8116600
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.625487
Development and Validation of Automated Visual Field Report Extraction Platform Using Computer Vision Tools
Abstract
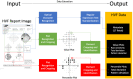
Purpose: To introduce and validate hvf_extraction_script, an open-source software script for the automated extraction and structuring of metadata, value plot data, and percentile plot data from Humphrey visual field (HVF) report images. Methods: Validation was performed on 90 HVF reports over three different report layouts, including a total of 1,530 metadata fields, 15,536 value plot data points, and 10,210 percentile data points, between the computer script and four human extractors, compared against DICOM reference data. Computer extraction and human extraction were compared on extraction time as well as accuracy of extraction for metadata, value plot data, and percentile plot data. Results: Computer extraction required 4.9-8.9 s per report, compared to the 6.5-19 min required by human extractors, representing a more than 40-fold difference in extraction speed. Computer metadata extraction error rate varied from an aggregate 1.2-3.5%, compared to 0.2-9.2% for human metadata extraction across all layouts. Computer value data point extraction had an aggregate error rate of 0.9% for version 1, <0.01% in version 2, and 0.15% in version 3, compared to 0.8-9.2% aggregate error rate for human extraction. Computer percentile data point extraction similarly had very low error rates, with no errors occurring in version 1 and 2, and 0.06% error rate in version 3, compared to 0.06-12.2% error rate for human extraction. Conclusions: This study introduces and validates hvf_extraction_script, an open-source tool for fast, accurate, automated data extraction of HVF reports to facilitate analysis of large-volume HVF datasets, and demonstrates the value of image processing tools in facilitating faster and cheaper large-volume data extraction in research settings.
Keywords: computer vision and image processing; glaucoma; neuroophthalmogy; optical character reader; visual field.
Copyright © 2021 Saifee, Wu, Liu, Ma, Patlidanon, Yu, Ying and Han.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Multifocal VEP and ganglion cell damage: applications and limitations for the study of glaucoma.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2003 Mar;22(2):201-51. doi: 10.1016/s1350-9462(02)00061-7. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2003. PMID: 12604058 Review.
-
Detecting early to mild glaucomatous damage: a comparison of the multifocal VEP and automated perimetry.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004 Feb;45(2):492-8. doi: 10.1167/iovs.03-0602. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004. PMID: 14744890
-
M&S Smart System Contrast Sensitivity Measurements Compared With Standard Visual Function Measurements in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma Patients.J Glaucoma. 2017 Jun;26(6):528-533. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0000000000000659. J Glaucoma. 2017. PMID: 28333894 Free PMC article.
-
Can Visual Field Progression be Predicted by Confocal Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopic Imaging of the Optic Nerve Head in Glaucoma? (An American Ophthalmological Society Thesis).Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2015;113:T4. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2015. PMID: 26549913 Free PMC article.
-
[Aiming for zero blindness].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2015 Mar;119(3):168-93; discussion 194. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2015. PMID: 25854109 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
UWHVF: A Real-World, Open Source Dataset of Perimetry Tests From the Humphrey Field Analyzer at the University of Washington.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022 Jan 3;11(1):2. doi: 10.1167/tvst.11.1.1. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 34978561 Free PMC article.
-
Visual Field Pointwise Analysis of the Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Weight Trial (IIH:WT).Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2023 May 1;12(5):1. doi: 10.1167/tvst.12.5.1. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 37126336 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
PyVisualFields: A Python Package for Visual Field Analysis.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2023 Feb 1;12(2):6. doi: 10.1167/tvst.12.2.6. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 36745440 Free PMC article.
-
Towards effective data sharing in ophthalmology: data standardization and data privacy.Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2022 Sep 1;33(5):418-424. doi: 10.1097/ICU.0000000000000878. Epub 2022 Jul 12. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35819893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Machine Learning Applied to Visual Fields of Dominant Optic Atrophy Patients.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2025 Jun 2;14(6):20. doi: 10.1167/tvst.14.6.20. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2025. PMID: 40492996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carl Zeiss Meditec AG. DICOM Conformance Statement - Forum Version 3.2. Available online at: https://www.zeiss.com/content/dam/Meditec/downloads/pdf/DICOM/DICOM_Conf... (accessed November 3, 2020).
-
- Norman DA. Design rules based on analyses of human error. Commun ACM. (1983) 26:254-8. 10.1145/2163.358092 - DOI
-
- Soboczenski F. The Effect of Interface Elements on Transcription Tasks to Reduce Number-Entry Errors. (2014). Availble online at: http://etheses.whiterose.ac.uk/11775/1/thesis.pdf (accessed November 3, 2020).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

