Investigating the Possibility of Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Vaccinium arctostaphlyos Extract and Evaluating Its Antibacterial Properties
- PMID: 33997013
- PMCID: PMC8110411
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5572252
Investigating the Possibility of Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Vaccinium arctostaphlyos Extract and Evaluating Its Antibacterial Properties
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Investigating the Possibility of Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Vaccinium arctostaphlyos Extract and Evaluating Its Antibacterial Properties.Biomed Res Int. 2024 Mar 20;2024:9835064. doi: 10.1155/2024/9835064. eCollection 2024. Biomed Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38550136 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: Vaccinium genus plants have medicinal value, of which Vaccinium arctostaphylos (Caucasian whortleberry or Qare-Qat in the local language) is the only available species in Iran. Public tendency to use herbal remedies and natural products such as synthesized nanoparticles is increasing due to the proof of the destructive side effects of chemical drugs. Nanosilver products have been effective against more than 650 microbe types. This study was aimed at assessing the possibility of green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Vaccinium arctostaphylos aqueous extract and at evaluating its antibacterial properties, as well.
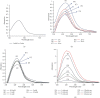
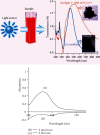
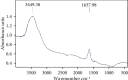
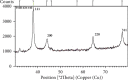
Materials and methods: In order to synthesize silver nanoparticles, different volumes of Vaccinium arctostaphylos aqueous extract (3, 5, 10, 15, and 30 ml) were assessed with different silver nitrate solution concentrations (0.5, 1, 3, 5, and 10 mM) and different reaction time durations (1, 3, 5, 10, and 20 minutes) at room temperature using a rotary shaker with a speed of 150 rpm. Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were carried out. The antibacterial activity of the aqueous extract and the synthesized nanoparticles was evaluated, as well.
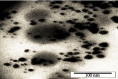
Results: Silver nanoparticle formation process was confirmed with XRD analysis, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and FTIR spectroscopy. The UV-Vis spectroscopy of silver colloidal nanoparticles showed a surface plasmon resonance peak at 443 nm under optimal conditions (3 ml aqueous extract volume, 1 mM silver nitrate solution concentration, and 3 min reaction time under sunlight exposure). The reduction of silver ions to silver nanoparticles in solution was confirmed, as well. Based on X-ray diffraction analysis, the size of silver nanoparticles was in the range of 7-16 nm. TEM images showed an even distribution of silver nanoparticles, with a spherical shape. FTIR spectroscopy demonstrated the presence of different functional groups of oxygenated compounds such as carboxyl, hydroxyl, and nitrogenous groups. The antibacterial properties of the synthesized nanoparticles were confirmed.
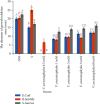
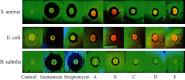
Conclusion: The synthesized nanoparticles showed more antibacterial properties against gram-positive bacteria (Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus) than gram-negative ones (Escherichia coli and Salmonella enteritidis).
Copyright © 2021 Sedighe Khodadadi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Lateef A., Ojo S. A., Elegbede J. A. The emerging roles of arthropods and their metabolites in the green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Nanotechnology Reviews. 2016;5(6):601–622. doi: 10.1515/ntrev-2016-0049. - DOI
-
- Singh M., Singh S., Prasad S., Gambhir I. Nanotechnology in medicine and antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles. Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures. 2008;3(3):115–122.
-
- Gericke M., Pinches A. Biological synthesis of metal nanoparticles. Hydrometallurgy. 2006;83(1-4):132–140. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2006.03.019. - DOI
-
- Nadagouda M. N., Hoag G., Collins J., Varma R. S. Green synthesis of Au nanostructures at room temperature using biodegradable plant surfactants. Crystal Growth & Design. 2009;9(11):4979–4983. doi: 10.1021/cg9007685. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

