The Natural History and Reperfusion Therapy Outcomes of Acute Ischemic Stroke due to Isolated M2 Occlusions
- PMID: 33997031
- PMCID: PMC8096556
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6626604
The Natural History and Reperfusion Therapy Outcomes of Acute Ischemic Stroke due to Isolated M2 Occlusions
Abstract
Objective: Currently, the standard treatment modality for patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) presenting with isolated M2 occlusions is not specific. We therefore assessed the difference in treatment outcomes for patients with isolated M2 occlusions.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed consecutive patients with AIS presenting with isolated M2 occlusions from October 1, 2018, to June 30, 2020. Patients were divided into 3 groups based on the treatments they received: no reperfusion therapy (NRT), intravenous thrombolysis treatment (IVT), and endovascular intervention (EVT), which comprised IVT in conjunction with EVT or EVT alone. The primary outcomes were improvements in modified Rankin Scale (mRS) scores at 90 days and National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) scores at 24 hours after treatment compared with the baseline. The secondary efficacy outcome comprised a good outcome rate defined as a 90 - day mRS score ≤ 2, final infarct volume (FIV), 90-day mortality rate, and successful recanalization rate, which was defined as a modified thrombolysis in cerebral infarction score ≥ 2b. Safety outcomes included symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage and procedure-related complications.
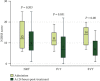
Results: Seventy patients were enrolled and divided into 3 groups: the NRT group (n = 25), IVT group (n = 27), and EVT group (n = 18). Twenty-four-hour posttreatment NIHSS scores were substantially decreased by EVT compared with NRT (adjusted β -4.01, 95% confidence interval [CI] -6.60 to -1.43; P = 0.003) or IVT (adjusted β, -3.61 [95% CI, -6.45 to -0.77]; P = 0.013). Compared with the outcomes observed after NRT, patients who received EVT were more likely to achieve lower 90-day mRS scores (adjusted β, -1.42 [95% CI, -2.66 to -0.63]; P = 0.007), higher good outcome rates (adjusted odds ratio, 8.73 [95% CI, 1.43-53.24]; P = 0.019), and smaller FIVs (adjusted β, -29.66 [95% CI, -59.73 to 0.42]; P = 0.048). The recanalization rate of EVT was high (88.89%), and procedure-related complications were rare (5.56%).
Conclusions: For acute, isolated M2 occlusions, EVT could dramatically and rapidly improve neurological deficits with high safety and effectiveness. These changes were observed at 24 hours after treatment and were maintained over the long term.
Copyright © 2021 Hongmin Gong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of final infarct volumes in patients who received endovascular therapy or intravenous thrombolysis for acute intracranial large-vessel occlusions.JAMA Neurol. 2013 Jul;70(7):831-6. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.413. JAMA Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23699864
-
Intravenous Thrombolysis before Complete Angiographic Reperfusion: Beyond Angiographic Assessment to Target Microvascular Obstruction?Ann Neurol. 2024 Apr;95(4):762-773. doi: 10.1002/ana.26867. Epub 2024 Jan 10. Ann Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38148607
-
Endovascular Thrombectomy Outcomes with and without Intravenous Thrombolysis for Large Ischemic Cores Identified with CT or MRI.Radiology. 2023 Oct;309(1):e230440. doi: 10.1148/radiol.230440. Radiology. 2023. PMID: 37847131
-
Endovascular thrombectomy with or without intravenous thrombolysis in acute basilar artery occlusion ischemic stroke: A meta-analysis.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2022 Dec;31(12):106847. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2022.106847. Epub 2022 Oct 28. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2022. PMID: 36323166
-
Reperfusion strategies in stroke due to isolated cervical internal carotid artery occlusion: systematic review and treatment comparison.Neurol Sci. 2021 Jun;42(6):2301-2308. doi: 10.1007/s10072-020-04735-5. Epub 2020 Oct 10. Neurol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33037515 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Endovascular treatment achieves better outcomes than best medical management in patients with M2 occlusion and high stroke severity: a meta-analysis.J Neurol. 2023 Jun;270(6):2924-2937. doi: 10.1007/s00415-023-11653-x. Epub 2023 Mar 2. J Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36862149 Review.
-
Mechanical Thrombectomy for Pediatric Arterial Ischemic Stroke from Acute M2 Occlusion.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2024 May 9;45(5):588-591. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A8182. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2024. PMID: 38548309 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

