Prognostic utility of pretreatment neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in survival outcomes in localized non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy: Selection of an ideal clinical cutoff point
- PMID: 33997320
- PMCID: PMC8089768
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ctro.2021.03.010
Prognostic utility of pretreatment neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in survival outcomes in localized non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy: Selection of an ideal clinical cutoff point
Abstract
Background and purpose: Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) has been associated with overall survival (OS) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). We aimed to assess the utility of NLR as a predictor of lung cancer-specific survival (LCS) and identify an optimal, pretreatment cutoff point in patients with localized NSCLC treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) within the Veterans Affairs' (VA) national database.
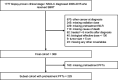
Materials and methods: In the VA database, we identified patients with biopsy-proven, clinical stage I NSCLC treated with SBRT between 2006 and 2015. Cutoff points for NLR were calculated using Contal/O'Quigley's and Cox Wald methods. Primary outcomes of OS, LCS, and non-lung cancer survival (NCS) were evaluated in Cox and Fine-Gray models.
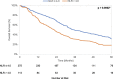
Results: In 389 patients, optimal NLR cutoff was identified as 4.0. In multivariable models, NLR > 4.0 was associated with decreased OS (HR 1.44, p = 0.01) and NCS (HR 1.68, p = 0.01) but not with LCS (HR 1.32, p = 0.09). In a subset analysis of 229 patients with pulmonary function tests, NLR > 4.0 remained associated with worse OS (HR 1.51, p = 0.02) and NCS (HR 2.18, p = 0.01) while the association with LCS decreased further (HR 1.22, p = 0.39).
Conclusion: NLR was associated with worse OS in patients with localized NSCLC treated with SBRT; however, NLR was only associated with NCS and not with LCS. Pretreatment NLR, with a cutoff of 4.0, offers potential as a marker of competing mortality risk which can aid in risk stratification in this typically frail and comorbid population. Further studies are needed to validate pretreatment NLR as a clinical tool in this setting.
Keywords: LCS, lung cancer-specific survival; NCS, non-lung cancer survival; NLR, Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio; Non-small cell lung cancer; OS, overall survival; Prognostic factors; SBRT, stereotactic body radiotherapy; Stereotactic body radiotherapy; VA, Veterans Affairs; Veterans affairs (U.S.).
© 2021 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2016, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD, https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2016/, based on November 2018 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, April 2019.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

