Microbiological Testing for Coronavirus Disease 2019
- PMID: 33997438
- PMCID: PMC8119126
- DOI: 10.31662/jmaj.2021-0012
Microbiological Testing for Coronavirus Disease 2019
Abstract
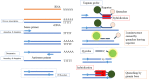
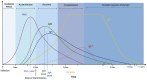
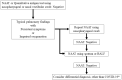
Microbiological diagnosis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is mainly performed through nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) and antigen test. Although NAAT is the standard diagnostic test, its use is limited by insufficient laboratory resources and long turnaround time. Point-of-care NAAT tests have been introduced to address these shortcomings, but their varied sensitivity and resource constraints remain a concern. Antigen tests require fewer resources but have low sensitivity. Nevertheless, low-sensitivity tests may be useful depending on the situation. In contrast, in some clinical phases of COVID-19, high-sensitivity tests may provide false-negative results. Therefore, the right testing strategy is needed for an accurate diagnosis. In this review, the characteristics and clinical applications of microbiological tests available in Japan (NAAT, antigen test, and antibody test) are discussed. The clinical diagnosis of COVID-19 is slightly complicated, and cases in which the infection spreads from asymptomatic infected individuals are many; hence, laboratory diagnosis is essential to prevent further transmission.
Keywords: COVID-19; Japan; antigen test; microbiological test; nucleic acid detection test.
Copyright © Japan Medical Association.
Conflict of interest statement
K.Y. received research grants from Fujirebio, Inc., Mizuho Medy, Co., Ltd., and VisGene Inc.; N.O. received grants from Sanofi Pasteur and Eiken Chemical Co., Ltd., outside the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- NIID-J. Validation of SARS-CoV-2 gene testing method in which clinical evaluation results were obtained using clinical specimens [Internet]. [updated 2020 Oct 23; cited 2001 Jan 25]. Available from: https://www.niid.go.jp/niid/images/lab-manual/2019-nCoV-17-current.pdf. Japanese.
-
- MHLW. List of authorized In Vitro Diagnostics (IVDs) for COVID-19 [Internet]. [updated 2001 Jan 22; cited 2021 Jan 25]. Available from: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_11332.html.
-
- MHLW. Guideline on the diagnosis of COVID-19, 3rd ed [Internet]. [cited 2021 Jan 25]. Available from: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/content/000725966.pdf. Japanese.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
