MoS2-based nanocomposites for cancer diagnosis and therapy
- PMID: 33997503
- PMCID: PMC8102209
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.04.021
MoS2-based nanocomposites for cancer diagnosis and therapy
Abstract
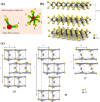
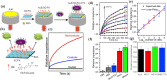
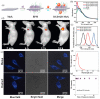
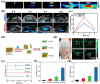
Molybdenum is a trace dietary element necessary for the survival of humans. Some molybdenum-bearing enzymes are involved in key metabolic activities in the human body (such as xanthine oxidase, aldehyde oxidase and sulfite oxidase). Many molybdenum-based compounds have been widely used in biomedical research. Especially, MoS2-nanomaterials have attracted more attention in cancer diagnosis and treatment recently because of their unique physical and chemical properties. MoS2 can adsorb various biomolecules and drug molecules via covalent or non-covalent interactions because it is easy to modify and possess a high specific surface area, improving its tumor targeting and colloidal stability, as well as accuracy and sensitivity for detecting specific biomarkers. At the same time, in the near-infrared (NIR) window, MoS2 has excellent optical absorption and prominent photothermal conversion efficiency, which can achieve NIR-based phototherapy and NIR-responsive controlled drug-release. Significantly, the modified MoS2-nanocomposite can specifically respond to the tumor microenvironment, leading to drug accumulation in the tumor site increased, reducing its side effects on non-cancerous tissues, and improved therapeutic effect. In this review, we introduced the latest developments of MoS2-nanocomposites in cancer diagnosis and therapy, mainly focusing on biosensors, bioimaging, chemotherapy, phototherapy, microwave hyperthermia, and combination therapy. Furthermore, we also discuss the current challenges and prospects of MoS2-nanocomposites in cancer treatment.
Keywords: Bioimaging; Biosensor; Cancer; Chemotherapy; Combination therapy; Microwave hyperthermia; MoS2; Phototherapy.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures











Similar articles
-
Molybdenum Disulfide Nanocomposites for Cancer Diagnosis and Therapeutics: Biosensors, Bioimaging, and Phototherapy.Adv Healthc Mater. 2025 May;14(14):e2500655. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202500655. Epub 2025 Apr 27. Adv Healthc Mater. 2025. PMID: 40289409 Review.
-
Functionalized MoS2-erlotinib produces hyperthermia under NIR.J Nanobiotechnology. 2019 Jun 19;17(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12951-019-0508-9. J Nanobiotechnology. 2019. PMID: 31217009 Free PMC article.
-
A multifunctional nanoplatform based on MoS2-nanosheets for targeted drug delivery and chemo-photothermal therapy.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020 Jan 1;185:110585. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110585. Epub 2019 Oct 17. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020. PMID: 31683203
-
Rod-shape MSN@MoS2 Nanoplatform for FL/MSOT/CT Imaging-Guided Photothermal and Photodynamic Therapy.Theranostics. 2019 May 31;9(14):3992-4005. doi: 10.7150/thno.32715. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31281527 Free PMC article.
-
Molybdenum-based hetero-nanocomposites for cancer therapy, diagnosis and biosensing application: Current advancement and future breakthroughs.J Control Release. 2021 Feb 10;330:257-283. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.12.015. Epub 2020 Dec 18. J Control Release. 2021. PMID: 33345832 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Sonodynamic Therapy-Based Nanomedicines for Cancer Immunotherapy.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Jan;10(2):e2204365. doi: 10.1002/advs.202204365. Epub 2022 Nov 27. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 36437106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomaterials in Targeting Cancer Cells with Nanotherapeutics: Transitioning Towards Responsive Systems.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(38):3018-3037. doi: 10.2174/0113816128317407240724065912. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 39143881 Review.
-
An Update on Graphene Oxide: Applications and Toxicity.ACS Omega. 2022 Sep 28;7(40):35387-35445. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c03171. eCollection 2022 Oct 11. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36249372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidic Synthesis of the Tumor Microenvironment-Responsive Nanosystem for Type-I Photodynamic Therapy.Molecules. 2022 Dec 1;27(23):8386. doi: 10.3390/molecules27238386. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36500477 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress in Exosome-Based Nanoscale Drug Carriers in Tumor Therapies.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 21;12:919279. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.919279. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35800056 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bray F., Ferlay J., Soerjomataram I., Siegel R.L., Torre L.A., Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J., Colombet M., Soerjomataram I., Mathers C., Parkin D.M. Vol. 144. 2019. pp. 1941–1953. (Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods). 8. - PubMed
-
- Hu Y., Mignani S., Majoral J.P., Shen M., Shi X. Construction of iron oxide nanoparticle-based hybrid platforms for tumor imaging and therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018;47(5):1874–1900. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

