Photoactivatable nanogenerators of reactive species for cancer therapy
- PMID: 33997507
- PMCID: PMC8105601
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.04.030
Photoactivatable nanogenerators of reactive species for cancer therapy
Abstract
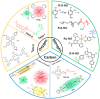
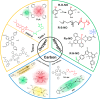
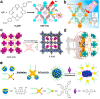
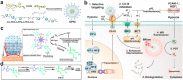
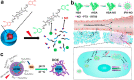
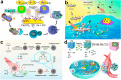
In recent years, reactive species-based cancer therapies have attracted tremendous attention due to their simplicity, controllability, and effectiveness. Herein, we overviewed the state-of-art advance for photo-controlled generation of highly reactive radical species with nanomaterials for cancer therapy. First, we summarized the most widely explored reactive species, such as singlet oxygen, superoxide radical anion (O2 ●-), nitric oxide (●NO), carbon monoxide, alkyl radicals, and their corresponding secondary reactive species generated by interaction with other biological molecules. Then, we discussed the generating mechanisms of these highly reactive species stimulated by light irradiation, followed by their anticancer effect, and the synergetic principles with other therapeutic modalities. This review might unveil the advantages of reactive species-based therapeutic methodology and encourage the pre-clinical exploration of reactive species-mediated cancer treatments.
Keywords: Alkyl radicals; Carbon monoxide; Phototherapy; Reactive nitrogen species; Reactive oxygen species.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Gas-Mediated Cancer Bioimaging and Therapy.ACS Nano. 2019 Oct 22;13(10):10887-10917. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b04954. Epub 2019 Sep 27. ACS Nano. 2019. PMID: 31538764
-
Automatic flow injection based methodologies for determination of scavenging capacity against biologically relevant reactive species of oxygen and nitrogen.Talanta. 2009 Jun 15;78(4-5):1219-26. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2009.02.006. Epub 2009 Feb 13. Talanta. 2009. PMID: 19362179 Review.
-
Carbon nanodots with a controlled N structure by a solvothermal method for generation of reactive oxygen species under visible light.Luminescence. 2023 Feb;38(2):127-135. doi: 10.1002/bio.4428. Epub 2023 Jan 7. Luminescence. 2023. PMID: 36581317
-
The complex interplay of iron metabolism, reactive oxygen species, and reactive nitrogen species: insights into the potential of various iron therapies to induce oxidative and nitrosative stress.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Dec;65:1174-1194. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.09.001. Epub 2013 Sep 12. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 24036104 Review.
-
[Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in inflammatory process].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2007 Aug;23(134):131-6. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2007. PMID: 18044345 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Autophagy Regulation Using Multimodal Chlorin e6-Loaded Polysilsesquioxane Nanoparticles to Improve Photodynamic Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2023 May 20;15(5):1548. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051548. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37242794 Free PMC article.
-
Li-Doped Bioactive Ceramics: Promising Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine.J Funct Biomater. 2022 Sep 24;13(4):162. doi: 10.3390/jfb13040162. J Funct Biomater. 2022. PMID: 36278631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Glutathione Depletion-Enhanced Porphyrin-Based nMOFs for Photodynamic Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Feb 12;17(2):244. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17020244. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40006611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomaterials-Induced Redox Imbalance: Challenged and Opportunities for Nanomaterials in Cancer Therapy.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Apr;11(16):e2308632. doi: 10.1002/advs.202308632. Epub 2024 Feb 21. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38380505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Porphyrin-Based Covalent Organic Frameworks for Synergistic Photodynamic and Photothermal Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Dec 22;16(12):1625. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16121625. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39771603 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lucky S.S., Soo K.C., Zhang Y. Nanoparticles in photodynamic therapy. Chem. Rev. 2015;115:1990–2042. - PubMed
-
- He X., Yang Y., Guo Y., Lu S., Du Y., Li J.-J., Zhang X., Leung N.L.C., Zhao Z., Niu G., Yang S., Weng Z., Kwok R.T.K., Lam J.W.Y., Xie G., Tang B.Z. Phage-guided targeting, discriminative imaging, and synergistic killing of bacteria by aie bioconjugates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020;142:3959–3969. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

