Photoactivatable nanogenerators of reactive species for cancer therapy
- PMID: 33997507
- PMCID: PMC8105601
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.04.030
Photoactivatable nanogenerators of reactive species for cancer therapy
Abstract
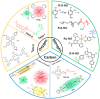
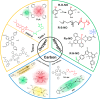
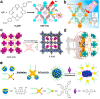
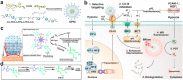
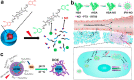
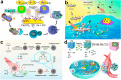
In recent years, reactive species-based cancer therapies have attracted tremendous attention due to their simplicity, controllability, and effectiveness. Herein, we overviewed the state-of-art advance for photo-controlled generation of highly reactive radical species with nanomaterials for cancer therapy. First, we summarized the most widely explored reactive species, such as singlet oxygen, superoxide radical anion (O2 ●-), nitric oxide (●NO), carbon monoxide, alkyl radicals, and their corresponding secondary reactive species generated by interaction with other biological molecules. Then, we discussed the generating mechanisms of these highly reactive species stimulated by light irradiation, followed by their anticancer effect, and the synergetic principles with other therapeutic modalities. This review might unveil the advantages of reactive species-based therapeutic methodology and encourage the pre-clinical exploration of reactive species-mediated cancer treatments.
Keywords: Alkyl radicals; Carbon monoxide; Phototherapy; Reactive nitrogen species; Reactive oxygen species.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Lucky S.S., Soo K.C., Zhang Y. Nanoparticles in photodynamic therapy. Chem. Rev. 2015;115:1990–2042. - PubMed
-
- He X., Yang Y., Guo Y., Lu S., Du Y., Li J.-J., Zhang X., Leung N.L.C., Zhao Z., Niu G., Yang S., Weng Z., Kwok R.T.K., Lam J.W.Y., Xie G., Tang B.Z. Phage-guided targeting, discriminative imaging, and synergistic killing of bacteria by aie bioconjugates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020;142:3959–3969. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

