Role of hyaluronic acid intrauterine injection in the prevention of Asherman's syndrome in women undergoing uterine septum resection: An RCT
- PMID: 33997593
- PMCID: PMC8106814
- DOI: 10.18502/ijrm.v19i4.9060
Role of hyaluronic acid intrauterine injection in the prevention of Asherman's syndrome in women undergoing uterine septum resection: An RCT
Abstract
Background: Adhesion due to intrauterine surgery such as septal resection associated with damaged endometrium can increase the risk of Asherman's syndrome. The main goal of treatment in this syndrome is to repair the damaged endometrium for creating a physiological pregnancy.
Objective: To investigate the effect of intrauterine injection of hyaluronic acid on the prevention of Asherman's syndrome in women undergoing uterine septum resection.
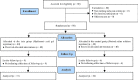
Materials and methods: In this double-blind randomized clinical trial, 65 women undergoing the uterine septum resection were divided into two groups; the case group (n = 34) and the control group (n = 31). Immediately after the septal resection with a resectoscope, 1cc of hyaluronic acid gel in the case group and 1cc normal saline solution as a placebo in the control group was injected into the uterine cavity. After two months, existence of intrauterine adhesions in the both groups was examined by the hysteroscope and assessment of menstrual patterns, according to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine criteria.
Results: Our results showed that after intervention, the incidence of Asherman's syndrome in the control group was higher than the case group (p = 0.012). In the case group, only four women had poor adhesion (Asherman's syndrome) at the end of the study, while the rest of them were free of any adhesions in the uterine cavity. In the control group, however, only 19 were free of intrauterine adhesions and 12 had mild symptoms.
Conclusion: The results of the study exhibited the hyaluronic acid capacity to reduce the risk of Asherman's syndrome in women with endometrial damage following a septal resection surgery.
Keywords: Hyaluronic acid; Resection.; Septum; Uterine; Asherman's syndrome.
Copyright © 2021 Ghanadzadeh Tafti et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest with regard to the present study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A matched cohort study comparing the outcome of intrauterine adhesiolysis for Asherman's syndrome after uterine artery embolization or surgical trauma.J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2014 Nov-Dec;21(6):1022-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2014.04.015. Epub 2014 May 16. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2014. PMID: 24842805
-
Restoring Fertility of Patients with Severe Asherman's Syndrome in the Office Setting: A Step-by-Step Recipe for Success.J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2023 May;30(5):355-356. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2023.02.002. Epub 2023 Feb 9. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2023. PMID: 36764649
-
A comparison of the treatment outcome of Asherman's syndrome which developed within and outside the puerperal period: A matched cohort study.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2025 Apr;104(4):774-780. doi: 10.1111/aogs.15057. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2025. PMID: 39968669 Free PMC article.
-
Endometrial Regeneration in Asherman's Syndrome: Clinical and Translational evidence of Stem Cell Therapies.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;14(6):454-459. doi: 10.2174/1574888X14666190213100528. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 30760192 Review.
-
Asherman's syndrome: current perspectives on diagnosis and management.Int J Womens Health. 2019 Mar 20;11:191-198. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S165474. eCollection 2019. Int J Womens Health. 2019. PMID: 30936754 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Application of Bioactive Hydrogels for Functional Treatment of Intrauterine Adhesion.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Sep 21;9:760943. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.760943. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34621732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclical endometrial repair and regeneration: Molecular mechanisms, diseases, and therapeutic interventions.MedComm (2020). 2023 Dec 1;4(6):e425. doi: 10.1002/mco2.425. eCollection 2023 Dec. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 38045828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent progress of Bioinspired Hydrogel-based delivery system for endometrial repair.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Sep 9;10:1013217. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1013217. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36159661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of auto-cross-linked hyaluronic gel to prevent intrauterine adhesion after hysteroscopic electrosurgical resection: a multi-center randomized controlled trial.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Nov;10(22):1217. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-4988. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36544634 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Methylprednisolone and Hyaluronic Acid on the Endometrium in Experimentally Induced Asherman Syndrome Rat Models: A Prospective Laboratory Study.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Mar 10;61(3):482. doi: 10.3390/medicina61030482. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40142293 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources