A Digital Filter-Based Method for Diagnosing Speech Comprehension Deficits
- PMID: 33997624
- PMCID: PMC8105531
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2020.09.007
A Digital Filter-Based Method for Diagnosing Speech Comprehension Deficits
Abstract
Objective: To improve the diagnostic efficiency of current tests for auditory processing disorders (APDs) by creating new test signals using digital filtering methods.
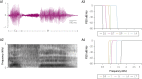
Methods: We conducted a prospective study from August 1, 2014, to August 31, 2019, using 3 low speech redundancy tests with novel test signals that we created with specially designed digital filters: the binaural resynthesis test and the low pass and high pass filtered speech tests. We validated and optimized these new tests, then applied them to healthy individuals across different age groups to examine how age affected performance and to children with APD before and after acoustically controlled auditory training (ACAT) to assess clinical improvement after treatment.
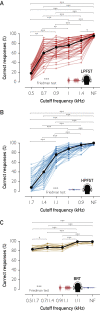
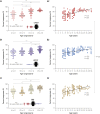
Results: We found a progressive increase in performance accuracy with less restrictive filters (P<.001) and with increasing age for all tests (P<.001). Our results suggest that binaural resynthesis and auditory closure mature at similar rates. We also demonstrate that the new tests can be used for the diagnosis of APD and for the monitoring of ACAT effects. Interestingly, we found that patients having the most severe deficits also benefited the most from ACAT (P<.001).
Conclusion: We introduce a method that substantially improves current diagnostic tools for APD. In addition, we provide information on auditory processing maturation in normal development and validate that our method can detect APD-related deficits and ACAT-induced improvements in auditory processing.
Keywords: AC, auditory closure; ACAT, acoustically controlled auditory training; APD, auditory processing disorder; BR, binaural resynthesis; BRT, binaural resynthesis test; FST, filtered speech test; HP, high pass; HPFST, high pass filtered speech test; L1, list 1; L2, list 2; LP, low pass; LPFST, low pass filtered speech test.
© 2020 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development of an adaptive low-pass filtered speech test for the identification of auditory processing disorders.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2012 Jun;76(6):777-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2012.02.039. Epub 2012 Mar 7. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2012. PMID: 22402015 Clinical Trial.
-
Assessment of auditory processing disorder in children using an adaptive filtered speech test.Int J Audiol. 2013 Oct;52(10):687-97. doi: 10.3109/14992027.2013.802380. Epub 2013 Jul 23. Int J Audiol. 2013. PMID: 23879742
-
The Effect of Varying Test Administration and Scoring Procedures on Three Tests of (Central) Auditory Processing Disorder.J Am Acad Audiol. 2019 Sep;30(8):694-702. doi: 10.3766/jaaa.17063. Epub 2019 Aug 16. J Am Acad Audiol. 2019. PMID: 31429399
-
Same or Different: The Overlap Between Children With Auditory Processing Disorders and Children With Other Developmental Disorders: A Systematic Review.Ear Hear. 2018 Jan/Feb;39(1):1-19. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000479. Ear Hear. 2018. PMID: 28863035 Free PMC article.
-
Auditory processing disorder and speech perception problems in noise: finding the underlying origin.Am J Audiol. 2010 Jun;19(1):17-25. doi: 10.1044/1059-0889(2010/09-0022). Epub 2010 Mar 22. Am J Audiol. 2010. PMID: 20308289 Review.
References
-
- American Academy of Audiology Clinical Practice Guidelines Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Children and Adults With Central Auditory Processing Disorder. August 2010. http://psha.org/pdfs/toolbox/CAPD-Guidelines_8-2010.pdf Accessed January 21, 2020.
-
- de Wit E., Visser-Bochane M.I., Steenbergen B., van Dijk P., van der Schans C.P., Luinge M.R. Characteristics of auditory processing disorders: a systematic review. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2016;59(2):384–413. - PubMed
-
- Pereira L.D., Schochat E. Pró-Fono; Barueri, SP, Brazil: 2015. Testes Auditivos Comportamentais para Avaliação do Processamento Auditivo Central.
-
- Ahmmed A.U. Intelligibility of degraded speech and the relationship between symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity/impulsivity and language impairment in children with suspected auditory processing disorder. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2017;101:178–185. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

