Entorhinal mismatch: A model of self-supervised learning in the hippocampus
- PMID: 33997671
- PMCID: PMC8091892
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102364
Entorhinal mismatch: A model of self-supervised learning in the hippocampus
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Entorhinal mismatch: A model of self-supervised learning in the hippocampus.iScience. 2021 May 17;24(5):102501. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102501. eCollection 2021 May 21. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34041451 Free PMC article.
Abstract
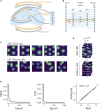
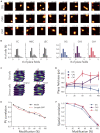
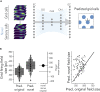
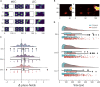
The hippocampal formation displays a wide range of physiological responses to different spatial manipulations of the environment. However, very few attempts have been made to identify core computational principles underlying those hippocampal responses. Here, we capitalize on the observation that the entorhinal-hippocampal complex (EHC) forms a closed loop and projects inhibitory signals "countercurrent" to the trisynaptic pathway to build a self-supervised model that learns to reconstruct its own inputs by error backpropagation. The EHC is then abstracted as an autoencoder, with the hidden layers acting as an information bottleneck. With the inputs mimicking the firing activity of lateral and medial entorhinal cells, our model is shown to generate place cells and to respond to environmental manipulations as observed in rodent experiments. Altogether, we propose that the hippocampus builds conjunctive compressed representations of the environment by learning to reconstruct its own entorhinal inputs via gradient descent.
Keywords: Cognitive Neuroscience; Neural Networks; Systems Neuroscience.
© 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

