Probiotic and resveratrol normalize GLP-1 levels and oxidative stress in the intestine of diabetic rats
- PMID: 33997755
- PMCID: PMC8091914
- DOI: 10.1016/j.metop.2021.100093
Probiotic and resveratrol normalize GLP-1 levels and oxidative stress in the intestine of diabetic rats
Abstract
Background: Recently, the use of incretins has been considered as a therapeutic target for diabetes. One of the important incretins in the improvement of diabetes is glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1), which is secreted by the gut and reduces the apoptosis of pancreatic β-cells and improves insulin sensitivity. In this experiment we determined the effects of resveratrol and probiotics on insulin resistance, oxidative stress, and GLP-1 in type 2 diabetes (T2D) rats.
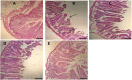
Methods: In this study, 40 male Wistar male rats were divided into 5 groups: 1. Control group, 2. T2D, 3. T2D treated with probiotics, 4. T2D treated with resveratrol, 5. T2D group treated with probiotics and resveratrol. After four weeks, the intestine were removed for histopathological analysis, biochemical tests, and oxidative stress markers.
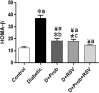
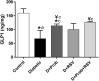
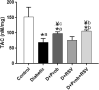
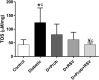
Results: Probiotics and resveratrol significantly decreased (p < 0.001) glucose and insulin resistance, and increased (p < 0.001) GLP1 and total antioxidant capacity compared to the diabetic group. Treatment with probiotics and resveratrol also returned intestinal histological changes in diabetic rats to normal.
Conclusion: Resveratrol and probiotics appear to be effective in controlling T2D by increasing GLP-1 levels and reducing oxidative stress.
Keywords: Glucagon-like peptide 1; Oxidative stress; Probiotics; Resveratrol; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2021 Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The entero-insular axis: implications for human metabolism.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2008;46(1):43-56. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2008.008. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2008. PMID: 18020966 Review.
-
Brain GLP-1/IGF-1 Signaling and Autophagy Mediate Exendin-4 Protection Against Apoptosis in Type 2 Diabetic Rats.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 May;55(5):4030-4050. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0622-3. Epub 2017 Jun 2. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28573460
-
[Incretins-adipocytokines interactions in type 2 diabetic subjects with or without non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: interest of GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) as a modulating biomarker].Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 2019 Jun 1;77(3):261-271. doi: 10.1684/abc.2019.1436. Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 2019. PMID: 30998190 French.
-
Composite probiotics alleviate type 2 diabetes by regulating intestinal microbiota and inducing GLP-1 secretion in db/db mice.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 May;125:109914. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109914. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32035395
-
Probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics and insulin sensitivity.Nutr Res Rev. 2018 Jun;31(1):35-51. doi: 10.1017/S095442241700018X. Epub 2017 Oct 17. Nutr Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 29037268 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical applications and mechanism insights of natural flavonoids against type 2 diabetes mellitus.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 16;10(9):e29718. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29718. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38694079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role and Mechanism of Probiotics Supplementation in Blood Glucose Regulation: A Review.Foods. 2024 Aug 27;13(17):2719. doi: 10.3390/foods13172719. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39272484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut-Microbial Metabolites, Probiotics and Their Roles in Type 2 Diabetes.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 27;22(23):12846. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312846. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of soymilk plus probiotics supplementation on cardiovascular risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized clinical trial.BMC Endocr Disord. 2023 Feb 10;23(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12902-023-01290-w. BMC Endocr Disord. 2023. PMID: 36759798 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Favorable effects of Anethum graveolens on liver oxidative stress and cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase levels in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) rat models.Metabol Open. 2021 Oct 14;12:100140. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2021.100140. eCollection 2021 Dec. Metabol Open. 2021. PMID: 34704009 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

