Nanotransducers for Wireless Neuromodulation
- PMID: 33997768
- PMCID: PMC8117115
- DOI: 10.1016/j.matt.2021.02.012
Nanotransducers for Wireless Neuromodulation
Abstract
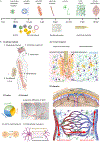
Understanding the signal transmission and processing within the central nervous system (CNS) is a grand challenge in neuroscience. The past decade has witnessed significant advances in the development of new tools to address this challenge. Development of these new tools draws diverse expertise from genetics, materials science, electrical engineering, photonics and other disciplines. Among these tools, nanomaterials have emerged as a unique class of neural interfaces due to their small size, remote coupling and conversion of different energy modalities, various delivery methods, and mitigated chronic immune responses. In this review, we will discuss recent advances in nanotransducers to modulate and interface with the neural system without physical wires. Nanotransducers work collectively to modulate brain activity through optogenetic, mechanical, thermal, electrical and chemical modalities. We will compare important parameters among these techniques including the invasiveness, spatiotemporal precision, cell-type specificity, brain penetration, and translation to large animals and humans. Important areas for future research include a better understanding of the nanomaterials-brain interface, integration of sensing capability for bidirectional closed-loop neuromodulation, and genetically engineered functional materials for cell-type specific neuromodulation.
Keywords: magnetic stimulation; nanotransducers; neuromodulation; optical stimulation; ultrasound modulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



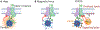
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
