Identifying key indicators of job loss trends during COVID-19 and beyond
- PMID: 33997770
- PMCID: PMC8112322
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ssaho.2021.100163
Identifying key indicators of job loss trends during COVID-19 and beyond
Abstract
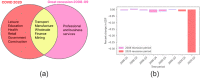
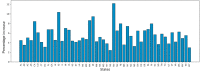
COVID-19, declared by the World Health Organization as a Public Health Emergency of International Concern, has claimed over 2.7 million lives worldwide. In the absence of vaccinations, social distancing and lockdowns emerged as the means to curb infection spread, with the downside of bringing the world economy to a standstill. In this work, we explore the epidemiological, socioeconomic and demographic factors affecting the unemployment rates of United States that may contribute towards policymaking to contain contagion and mortality while balancing the economy in the future. We identify the ethnic groups and job sectors that are affected by the pandemic and demonstrate that Gross Domestic Product (GDP), race, age group, lockdown severity and infected count are the key indicators of post-COVID job loss trends.
Keywords: COVID-19; Economy; Job loss; Policymaking; Regression.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- KFF Population distribution by race/ethnicity. 2018. https://www.kff.org/other/state-indicator/distribution-by-raceethnicity/
-
- Adhikari S., Meng S., Wu Y., Mao Y., Ye R., Wang Q., Sun C., Sylvia S., Rozelle S., Raat H., et al. Epidemiology, causes, clinical manifestation and diagnosis, prevention and control of coronavirus disease (covid-19) during the early outbreak period: A scoping review. Infectious diseases of poverty. 2020;9(1):1–12. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality . 2018. Health care quality: How does your state compare?https://www.ahrq.gov/data/infographics/state-compare-text.html
-
- Avila Y., Harvey B., Lee J., Mervosh S., Matthews A. The New York Times. See how all 50 states are reopening (and closing again) 2020. https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2020/us/states-reopen-map-coronaviru...
-
- Baker S., Bloom N., J Davis S., Terry S. National Bureau of Economic Research; 2020. Covid-induced economic uncertainty. Technical report.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
