Quantifying interfacial substrate interactions via surface energy analyses
- PMID: 33997808
- PMCID: PMC8091927
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2021.100476
Quantifying interfacial substrate interactions via surface energy analyses
Abstract
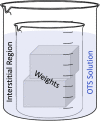
Determination of a substrate's surface energy profile is a facile and inexpensive method to indicate the substrate's interfacial thermodynamics with another substance (e.g., microorganisms, biomacromolecules, medical devices, etc). The following protocol details a goniometric method to calculate a substrate's surface energy profile which (1) directly correlates to a substrate's interfacial Gibbs energy (ΔG) and (2) predicts the interfacial interactions with other substances. We also provide a calculation template using advanced mathematics to expedite surface energy profile determination. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Cavitt et al. (2020).
Keywords: Biophysics; Energy; Material sciences; Microbiology; Physics.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Boo C., Hong S., Elimelech M. Relating organic fouling in membrane distillation to intermolecular adhesion forces and interfacial surface. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018;52:14198–14207. - PubMed
-
- Cavitt B. Mendeley Data, V1; 2021. Calculating the Five-Component Surface Energy Profile from Contact Angles (Goniometry)
-
- Gilman J.J. Direct measurements of the surface energies of crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 1960;31:2208–2218.
-
- Jaccodine R.J. Surface energy of germanium and silicon. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1963;110:524–527.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

