Discovery and development of trastuzumab deruxtecan and safety management for patients with HER2-positive gastric cancer
- PMID: 33997928
- PMCID: PMC8205906
- DOI: 10.1007/s10120-021-01196-3
Discovery and development of trastuzumab deruxtecan and safety management for patients with HER2-positive gastric cancer
Abstract
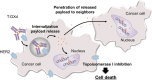
Approximately 12-15% of gastric cancers (GCs) are human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2)-positive (HER2 immunohistochemistry 3 + or 2 + /in situ hybridization + [ERBB2/CEP17 ≥ 2.0]). While the anti-HER2 monoclonal antibody trastuzumab, in combination with chemotherapy, is the standard treatment for HER2-positive GC, other HER2-targeted therapies have not demonstrated survival benefits in patients with GC, despite showing efficacy in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer. This indicates that there are unique challenges to the use of currently available HER2-targeted therapies for the treatment of HER2-positive GC. Trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) is an antibody-drug conjugate consisting of an anti-HER2 human monoclonal IgG1 antibody with the same amino acid sequence as trastuzumab, an enzymatically cleavable peptide-based linker, and DXd, a novel topoisomerase I inhibitor, as its released payload. T-DXd has a high drug-antibody ratio (approximately 8) and a demonstrated bystander antitumor effect. It has demonstrated significant efficacy when compared with standard therapies and is approved as third- or later-line treatment for HER2-positive GC in Japan and second- or later-line treatment in the US. T-DXd treatment is associated with gastrointestinal and hematological adverse events, and a risk of interstitial lung disease (ILD), with the ILD risk being higher in Japan than in countries other than Japan. However, most adverse events, including ILD, can be managed with proactive monitoring and T-DXd dose modification, and initiation of adequate treatment. In this review, we summarize the discovery and development of T-DXd and provide guidance for T-DXd safety management, including ILD monitoring, for patients with HER2-positive GC.
Keywords: Antibody–drug conjugate; Gastric cancer; HER-2; Review; Topoisomerase I inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
K Shitara reports paid consulting or advisory roles for Astellas, Eli Lilly, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Takeda, Pfizer, Ono, MSD, Taiho, Novartis, AbbVie, and GSK; honoraria from Novartis, AbbVie, and Yakult; and research funding from Astellas, Eli Lilly, Ono, Sumitomo Dainippon, Daiichi Sankyo, Taiho, Chugai, MSD, and Medi Science, outside the submitted work. E Baba reports grants and personal fees from Taiho, Chugai, Astellas, Merck Biopharma, Daiichi Sankyo, Ono, Kyowa-Kirin, Eisai, Eli Lilly, MSD, Sanofi, Yakult, and Takeda. K Fujitani reports personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Ono, Taiho, and Yakult. E Oki reports personal fees from Taiho, Takeda, Chugai, Eli Lilly, Ono, and Bayer. S Fujii has nothing to declare. K Yamaguchi reports grants and personal fees from Taiho, Chugai, Daiichi Sankyo, Ono, and Eli Lilly; personal fees from Takeda, Merck Serono, Bayer, and Bristol-Myers Squibb; and grants from MSD, Gilliad, Sumitomo Dainippon, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Sanofi.
Figures

References
-
- Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuire WL. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987;235(4785):177–182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

