The clinical significance of spondin 2 eccentric expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in bronchial asthma
- PMID: 33998076
- PMCID: PMC8183911
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.23764
The clinical significance of spondin 2 eccentric expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in bronchial asthma
Abstract
Background: Bronchial asthma (BA) was a heterogeneous disease characterized by chronic airway inflammation. Spondin 2 (SPON2) was reported to be implicated in the integrin pathway, protein metabolism, and drug-induced lupus erythematosus. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the significance of SPON2 in BA diagnosis and treatment.
Methods: Peripheral blood samples were obtained from 137 BA pediatric patients (61 mild-to-moderate BA and 76 severe BA) and 59 healthy children. Subject's information, clinical indexes, pulmonary ventilation functions were recorded in the two groups. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated from patients' samples. qRT-PCR and ELISA assays were employed to examine the levels of SPON2 and inflammatory cytokines, respectively. Pearson's correlation analysis confirmed the association between SPON2 and inflammatory cytokines. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was used to evaluate the potentials of SPON2 in terms of BA detection and discriminating against the severity of BA.
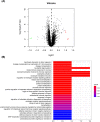
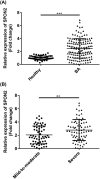
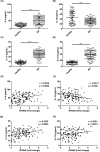
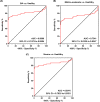
Results: Bioinformatics analysis showed that SPON2, OLFM4, XIST, and TSIX were significantly upregulated, while KDM5D and RPS4Y1 were reduced in BA. GO analysis verified that these six genes were mainly involved in neutrophil degranulation, neutrophil activation involved in immune response, neutrophil activation, and neutrophil-mediated immunity. After isolating PBMCs, we found that SPON2 was remarkably increased in BA pediatric group compared with healthy children, and the relative levels of SPON2 were related to the severity of BA. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis revealed the high potentials of SPON2 in BA diagnosis (AUC was 0.8080) and severity distinctions (AUCs were 0.7341 and 0.8541, respectively). Also, we found that there were significant differences in fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO), forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1)%, FEV1/ forced vital capacity (FVC)%, immunoglobulin E (IgE), serum eosinophils, and serum neutrophils between mild-to-moderate BA group and severe BA group. Finally, SPON2 was negatively correlated with IL-12 while positively associated with IL-4, IL-13, and IL-17A.
Conclusions: SPON2 was a viable biomarker for diagnosing and degree of severity in BA, providing more insight into exploring BA and treatment's pathogenesis.
Keywords: GO analysis; bronchial asthma; diagnosis; peripheral blood mononuclear cell; spondin 2.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The biological functions and related signaling pathways of SPON2.Front Oncol. 2024 Jan 9;13:1323744. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1323744. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38264743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic value of EOS count and serum VEGF in bronchial asthma and their correlation with inflammatory factors and lung function indicators.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 May 19;25(1):242. doi: 10.1186/s12890-025-03485-4. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 40389917 Free PMC article.
-
Expression patterns of serum miR-27a-3p and activating transcription factor 3 in children with bronchial asthma and their correlations with airway inflammation.Clin Respir J. 2025 Mar;19(3):e13631. doi: 10.1111/crj.13631. Epub 2023 Jun 29. Clin Respir J. 2025. PMID: 37385291 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) is a clinical indicator of uncontrolled asthma in children receiving inhaled corticosteroids.Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Jan;55(1):66-77. doi: 10.5414/CP202570. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 27443657 Clinical Trial.
-
Periostin as a biomarker for the diagnosis of pediatric asthma.Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2016 Aug;27(5):521-6. doi: 10.1111/pai.12575. Epub 2016 May 18. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27062336
Cited by
-
The role of lncRNA TSIX in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: mechanistic insights and clinical biomarker potential.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Nov 5;19(1):722. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05207-8. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39497068 Free PMC article.
-
The biological functions and related signaling pathways of SPON2.Front Oncol. 2024 Jan 9;13:1323744. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1323744. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38264743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fascial Pathophysiology in Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders and Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome: A Review of Emerging Evidence.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 11;26(12):5587. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125587. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spon2 knockdown suppresses the phenotype of house dust mite-induced allergic asthma in mice and cells.Immunol Res. 2025 Jul 21;73(1):109. doi: 10.1007/s12026-025-09641-6. Immunol Res. 2025. PMID: 40691739
-
Reactive Oxygen Species Mediate Transcriptional Responses to Dopamine and Cocaine in Human Cerebral Organoids.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 18;24(22):16474. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216474. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003664 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mims JW. Asthma: definitions and pathophysiology. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015;1:S2‐S6. - PubMed
-
- Liu G, Cooley MA, Nair PM, et al. Airway remodelling and inflammation in asthma are dependent on the extracellular matrix protein fibulin‐1c. J Pathol. 2017;242(4):510‐523. - PubMed
-
- Tagaya E, Tamaoki J. Mechanisms of airway remodeling in asthma. Allergol Int. 2007;56(4):331‐340. - PubMed
-
- Maslan J, Mims JW. What is asthma? Pathophysiology, demographics, and health care costs. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2014;47(1):13‐22. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

