Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor might exacerbate Graves' disease: A multicenter observational case-control study
- PMID: 33998766
- PMCID: PMC8565407
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.13578
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor might exacerbate Graves' disease: A multicenter observational case-control study
Abstract
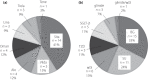
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4), namely CD26, is expressed on the surface of immune cells, suggesting that inhibition of DPP-4 might affect the immune system. The current multicenter observational case-control study was carried out to investigate the effects of DPP-4 inhibitor (DPP-4i) administration on Graves' disease (GD) activity. This study comprised patients with GD and type 2 diabetes, who were administered an oral hypoglycemic agent including DPP-4i. Exacerbation of GD was defined as an increase of antithyroid drug dose by 6 months after oral hypoglycemic agent administration. A total of 80 patients were enrolled and divided into an exacerbation group or a non-exacerbation group. The frequency of DPP-4i administration was significantly higher in the exacerbation group (88%) than that in the non-exacerbation group (31%). In multivariate logistic regression analysis, there was a significant association between DPP-4i administration and GD exacerbation (odds ratio 7.39). The current study suggests that DPP-4i administration is associated with GD exacerbation.
Keywords: Case-control study; Dipeptidyl peptidase-4; Graves' disease.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Diabetes Investigation published by Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes (AASD) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Akinobu Nakamura, Hideaki Miyoshi and Tatsuya Atsumi received honoraria for lectures and received research funding from some organizations as described below. There was no financial support for this study. Akinobu Nakamura received research funding from Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co. and Ono Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. Hideaki Miyoshi received honoraria for lectures from Astellas Pharma Inc., Dainippon Pharma Co., Eli Lilly, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., MSD, Novartis Pharma, Novo Nordisk Pharma, Kowa Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ono Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. and Sanofi, and received research funding from Astellas Pharma Inc., Daiichi Sankyo, Dainippon Pharma Co., Eli Lilly, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Novo Nordisk Pharma, Kowa Pharmaceutical Co., Abbott Japan Co., Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ono Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. and Taisho Toyama Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Tatsuya Atsumi received honoraria for lectures from Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Astellas Pharma Inc., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Pfizer Inc., AbbVie Inc., Eisai Co. Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd., Bristol‐Myers Squibb Co., UCB Japan Co. Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., and received research funding from Astellas Pharma Inc., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd., Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Pfizer Inc. and Alexion Inc. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Risk of Heart Failure in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Population-Based Cohort Study.Circ Heart Fail. 2017 Sep;10(9):e003957. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.117.003957. Circ Heart Fail. 2017. PMID: 28899989
-
Clinical features of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor-associated bullous pemphigoid in Japan: A nationwide retrospective observational study.J Dermatol. 2022 Jul;49(7):697-702. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.16394. Epub 2022 Apr 27. J Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35478414
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase 4-inhibitor treatment was associated with a reduced incidence of neoplasm in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of 115 randomized controlled trials with 121961 participants.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2022 Sep;31(9):957-964. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2022.2113056. Epub 2022 Aug 22. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35968648
-
Immunomodulatory activity of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in immune-related diseases.Eur J Immunol. 2023 Dec;53(12):e2250302. doi: 10.1002/eji.202250302. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Eur J Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37732495 Review.
-
DPP-4 inhibition and COVID-19: From initial concerns to recent expectations.Diabetes Metab. 2021 Mar;47(2):101213. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2020.11.005. Epub 2020 Nov 26. Diabetes Metab. 2021. PMID: 33249199 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The serum concentration and activity of DPP4 is positively related with the severity of hyperthyroidism in patients with Graves' disease.Ann Med. 2023 Dec;55(1):2226910. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2226910. Ann Med. 2023. PMID: 37350750 Free PMC article.
-
Updates of incretin-related drugs for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.J Diabetes Investig. 2023 Feb;14(2):189-192. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13945. Epub 2022 Nov 14. J Diabetes Investig. 2023. PMID: 36373430 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiological, Pathophysiological, and Clinical Considerations on the Interplay between Thyroid Disorders and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Nov 16;59(11):2013. doi: 10.3390/medicina59112013. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 38004062 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

