Benznidazole in vitro dissolution release from a pH-sensitive drug delivery system using Zif-8 as a carrier
- PMID: 33999312
- PMCID: PMC8128829
- DOI: 10.1007/s10856-021-06530-w
Benznidazole in vitro dissolution release from a pH-sensitive drug delivery system using Zif-8 as a carrier
Abstract
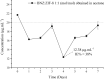
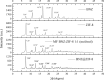
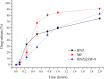
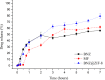
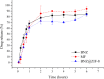
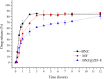
Chagas disease is a neglected tropical disease caused by the flagellate protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi (T. cruzi). Endemic in underdeveloped and developed countries, due to the migratory movement, it is considered a serious public health problem. Endemic in underdeveloped countries and due to the migratory movement, in developed countries as well, it is considered a serious public health problem. One of the reasons for this is a weak therapeutic arsenal, represented only by the drug benznidazole (BNZ) which, although it promotes significant cure rates in the acute phase of the disease, presents serious problems of toxicity and bioavailability, mainly due to its low aqueous solubility. Several studies have presented several drug delivery systems (DDS) based on BNZ aiming at enhancing its solubility in aqueous medium and, with this, promoting an increase in the dissolution rate and, consequently, in its bioavailability. However, the present work is a pioneer in using a zeolitic imidazolate framework as a carrier agent for a DDS in order to promote a pH-sensitive modulation of the drug. Thus, this work aimed to develop a novel DDS based on BNZ and the ZIF-8 to use it in development of prolonged-release dosage forms to alternative treatment of Chagas disease. The BNZ@ZIF-8 system was obtained through an ex situ method selected due to its higher incorporation efficiency (38%). Different characterization techniques corroborated the obtainment and drug release data were analyzed by in vitro dissolution assay under sink and non-sink conditions and setting the kinetic results through both model dependent and independent methods. Under sink conditions, at pH 4.5, BNZ and BNZ@ZIF-8 showed similar release profile, but the DDS was effective in promoting a prolonged release. At pH 7.6, after 7 h, BNZ showed a lower release than BNZ@ZIF-8. On the other hand, in non-sink conditions at pH 4.5 the BNZ presented 80% of drug release in 3 h, while the DDS in 6 h. At pH 7.6, BNZ presented a release of 80% in 2 h, while the DDS reaches it in only at 12 h. Therefore, at pH 4.5 the DDS BNZ@ZIF-8 showed a faster release with a burst effect, while at pH 7.6 it showed a prolonged and controlled release. Finally, it is evident that a promising DDS pH-sensitive was obtained as a novel carrier that might be able to prolongs BNZ release in dosage forms intended for the alternative treatment of Chagas disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ZIF-8 as a promising drug delivery system for benznidazole: development, characterization, in vitro dialysis release and cytotoxicity.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 8;10(1):16815. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73848-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33033328 Free PMC article.
-
Technological innovation strategies for the specific treatment of Chagas disease based on Benznidazole.Acta Trop. 2018 Sep;185:127-132. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.02.008. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Acta Trop. 2018. PMID: 29452113 Review.
-
Enhanced delivery of fixed-dose combination of synergistic antichagasic agents posaconazole-benznidazole based on amorphous solid dispersions.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018 Jul 1;119:208-218. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2018.04.024. Epub 2018 Apr 19. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018. PMID: 29679707
-
Novel solid dispersions of benznidazole: preparation, dissolution profile and biological evaluation as alternative antichagasic drug delivery system.Exp Parasitol. 2015 Feb;149:84-91. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Exp Parasitol. 2015. PMID: 25583295
-
From Benznidazole to New Drugs: Nanotechnology Contribution in Chagas Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 7;24(18):13778. doi: 10.3390/ijms241813778. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762080 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Organic solvent-free benznidazole nanosuspension as an approach to a novel pediatric formulation for Chagas disease.Ther Deliv. 2024;15(9):699-716. doi: 10.1080/20415990.2024.2380244. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Ther Deliv. 2024. PMID: 39101355 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Delivery of Gemcitabine for Precision Therapy of Cholangiocarcinoma Using Hyaluronic Acid-Modified Metal-Organic Framework Nanoparticles.ACS Omega. 2024 Feb 27;9(10):11998-12005. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c09751. eCollection 2024 Mar 12. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38496964 Free PMC article.
-
Cecropin-Loaded Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework Nanoparticles with High Biocompatibility and Cervical Cancer Cell Toxicity.Molecules. 2022 Jul 7;27(14):4364. doi: 10.3390/molecules27144364. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35889239 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-blastocystosis activity of antioxidant coated ZIF-8 combined with mesoporous silicas MCM-41 and KIT-6.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 17;12(1):6403. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-10397-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35431315 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomedicines against Chagas disease: a critical review.Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2024 Mar 27;15:333-349. doi: 10.3762/bjnano.15.30. eCollection 2024. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38590427 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kropf SP, Sá MR. The discovery of Trypanosoma cruzi and Chagas disease (1908–1909): tropical medicine in Brazil. História, Ciências, Saúde-Manguinhos. 2009;16:13–34. - PubMed
-
- Pérez-Molina JA, Sojo-Dorado J, Norman F, Monge-Maillo B, Díaz-Menéndez M, Albajar-Viñas P, et al. Nifurtimo x therapy for Chagas disease does not cause hypersensitivity reactions in patients with such previous adverse reactions during benznidazole treatment. Acta Trop. 2013;127:101–4. - PubMed
-
- Soares Sobrinho JL, Medeiros FPM, La Roca MF, Silva KER, Lima LNA, Rolim-Neto PJ. Delineamento de alternativas terapêuticas para o tratamento da doença de Chagas. Rev Patol Trop. 2007;36:103–18.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

