Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Regression by siRNA Delivered Through Exosomes That Display EGFR RNA Aptamer
- PMID: 33999716
- PMCID: PMC8591058
- DOI: 10.1089/nat.2021.0002
Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Regression by siRNA Delivered Through Exosomes That Display EGFR RNA Aptamer
Abstract
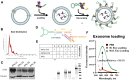
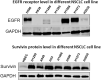
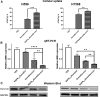
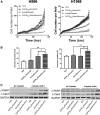
Lung cancer is the second most common cancer in both men and women and is the leading cause of cancer death in the United States. The development of drug resistance to commonly used chemotherapeutics in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) poses significant health risks and there is a dire need to improve patient outcomes. In this study, we report the use of RNA nanotechnology to display ligand on exosome that was loaded with small interfering RNA (siRNA) for NSCLC regression in animal trials. Cholesterol was used to anchor the ligand targeting epidermal growth factor receptor on exosomes that were loaded with siRNA to silence the antiapoptotic factor survivin. The cytosolic delivery of siRNA overcame the problem of endosome trapping, leading to potent gene knockdown, chemotherapy sensitization, and tumor regression, thus achieving a favorable IC50 of 20 nmol/kg siRNA encapsulated by exosome particles in the in vivo gene knockdown assessment.
Keywords: EGFR; RNA nanotechnology; aptamer; exosomes; non-small-cell lung cancer; siRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
P.G. is the consultant of Oxford Nanopore Technologies; the cofounder of Shenzhen P&Z Biomedical Co. Ltd., as well as the cofounder of ExonanoRNA, LLC and its subsidiary Weina Biomedical (Guangdong), Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chloroquine in combination with aptamer-modified nanocomplexes for tumor vessel normalization and efficient erlotinib/Survivin shRNA co-delivery to overcome drug resistance in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer.Acta Biomater. 2018 Aug;76:257-274. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.06.034. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 29960010
-
Anti-EGFR ScFv functionalized exosomes delivering LPCAT1 specific siRNAs for inhibition of lung cancer brain metastases.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Apr 8;22(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02414-7. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38589859 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic targeting of polo-like kinase 1 using RNA-interfering nanoparticles (iNOPs) for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 May 20;6(14):12020-34. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2664. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25557168 Free PMC article.
-
Role of exosomes in non-small cell lung cancer and EGFR-mutated lung cancer.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 12;14:1142539. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1142539. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37122754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small RNAs and non-small cell lung cancer.Curr Mol Med. 2006 May;6(3):339-49. doi: 10.2174/156652406776894554. Curr Mol Med. 2006. PMID: 16712479 Review.
Cited by
-
Ligand-displaying-exosomes using RNA nanotechnology for targeted delivery of multi-specific drugs for liver cancer regression.Nanomedicine. 2023 Jun;50:102667. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2023.102667. Epub 2023 Mar 21. Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 36948369 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome Enveloped by Nano Lipid Particle a New Model for Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Silencer Ribonucleic Acid Delivery System to a Glioblastoma Mice Model.Cancers (Basel). 2025 May 13;17(10):1648. doi: 10.3390/cancers17101648. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427146 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-derived small extracellular vesicles in cancer invasion and metastasis: molecular mechanisms, and clinical significance.Mol Cancer. 2024 Jan 19;23(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-01932-0. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38243280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Progress in Extracellular Vesicle-Based Carriers for Targeted Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jul 7;15(7):1902. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071902. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37514088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted delivery of RNAi to cancer cells using RNA-ligand displaying exosome.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023 Apr;13(4):1383-1399. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.11.019. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023. PMID: 37139430 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Duma N, Santana-Davila R and Molina JR. (2019). Non-small cell lung cancer: epidemiology, screening, diagnosis, and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc 94:1623–1640. - PubMed
-
- Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, Feng J, Liu XQ, Wang C, Zhang S, Wang J, Zhou S, et al. (2011). Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 12:735–742. - PubMed
-
- Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Sugawara S, Oizumi S, Isobe H, Gemma A, Harada M, Yoshizawa H, et al. (2010). Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med 362:2380–2388. - PubMed
-
- Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J, Reungwetwattana T, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, Dechaphunkul A, Imamura F, Nogami N, et al. (2018). Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 378:113–125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

