Endothelial glycocalyx during early reperfusion in patients undergoing cardiac surgery
- PMID: 33999952
- PMCID: PMC8128269
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0251747
Endothelial glycocalyx during early reperfusion in patients undergoing cardiac surgery
Abstract
Background: Experimental cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury causes degradation of the glycocalyx and coronary washout of its components syndecan-1 and heparan sulfate. Systemic elevation of syndecan-1 and heparan sulfate is well described in cardiac surgery. Still, the events during immediate reperfusion after aortic declamping are unknown both in the systemic and in the coronary circulation.
Methods: In thirty patients undergoing aortic valve replacement, arterial concentrations of syndecan-1 and heparan sulfate were measured immediately before and at one, five and ten minutes after aortic declamping (reperfusion). Parallel blood samples were drawn from the coronary sinus to calculate trans-coronary gradients (coronary sinus-artery).
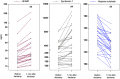
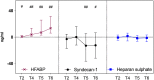
Results: Compared with immediately before aortic declamping, arterial syndecan-1 increased by 18% [253.8 (151.6-372.0) ng/ml vs. 299.1 (172.0-713.7) ng/ml, p < 0.001] but arterial heparan sulfate decreased by 14% [148.1 (135.7-161.7) ng/ml vs. 128.0 (119.0-138.2) ng/ml, p < 0.001] at one minute after aortic declamping. There was no coronary washout of syndecan-1 or heparan sulfate during reperfusion. On the contrary, trans-coronary sequestration of syndecan-1 occurred at five [-12.96 ng/ml (-36.38-5.15), p = 0.007] and at ten minutes [-12.37 ng/ml (-31.80-6.62), p = 0.049] after reperfusion.
Conclusions: Aortic declamping resulted in extracardiac syndecan-1 release and extracardiac heparan sulfate sequestration. Syndecan-1 was sequestered in the coronary circulation during early reperfusion. Glycocalyx has been shown to degrade during cardiac surgery. Besides degradation, glycocalyx has propensity for regeneration. The present results of syndecan-1 and heparan sulfate sequestration may reflect endogenous restoration of the damaged glycocalyx in open heart surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

