Early Impairment of Insulin Sensitivity, β-Cell Responsiveness, and Insulin Clearance in Youth with Stage 1 Type 1 Diabetes
- PMID: 34000022
- PMCID: PMC8372628
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgab344
Early Impairment of Insulin Sensitivity, β-Cell Responsiveness, and Insulin Clearance in Youth with Stage 1 Type 1 Diabetes
Abstract
Context: Clinical onset of type 1 diabetes (Stage 3 T1D) is preceded by a presymptomatic phase characterized by multiple islet autoantibodies with normal glucose tolerance (Stage 1 T1D).
Objective: The aim was to explore the metabolic phenotypes of β-cell function and insulin sensitivity and clearance in normoglycemic youth with Stage 1 T1D and compare them with healthy nonrelated peers during a 3-hour oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT).
Methods: Twenty-eight lean youth, 14 with ≥2 islet autoantibodies (cases) and 14 healthy controls underwent a 3-hour 9-point OGTT with measurement of glucose, C-peptide, and insulin. The oral minimal model was used to quantitate β-cell responsiveness (φtotal) and insulin sensitivity (SI), allowing assessment of β-cell function by the disposition index (DI=φtotal×SI). Fasting insulin clearance (CL0) was calculated as the ratio between the fasting insulin secretion rate (ISR) and plasma insulin levels (ISR0/I0), while postload clearance (CL180) was estimated by the ratio of AUC of ISR over the plasma insulin AUC for the 3-hour OGTT (ISRAUC/IAUC). Participants with impaired fasting glucose, impaired glucose tolerance, or any OGTT glucose concentration ≥200 mg/dL were excluded.
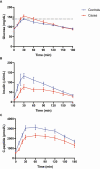
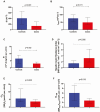
Results: Cases (10.5 years [8, 15]) exhibited reduced DI (P < .001) due to a simultaneous reduction in both φtotal (P < 0.001) and SI (P = .008) compared with controls (11.5 years [10.4, 14.9]). CL0 and CL180 were lower in cases than in controls (P = .005 and P = .019).
Conclusion: Presymptomatic Stage 1 T1D in youth is associated with reduced insulin sensitivity and lower β-cell responsiveness, and the presence of blunted insulin clearance.
Keywords: Prediabetes; insulin sensitivity; islet autoimmunity; oral minimal model; type 1 diabetes; β-cell function.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Keskinen P, Korhonen S, Kupila A, et al. . First-phase insulin response in young healthy children at genetic and immunological risk for Type I diabetes. Diabetologia. 2002;45(12):1639-1648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 DK085476/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK119800/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK127786/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX001733/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 DK114504/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK111038/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK097512/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK085476/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-0249139/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK045735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK127308/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD028016/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD040787/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085505/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002494/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK138335/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DK-045735/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK093954/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HD-40787/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK-111038/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

