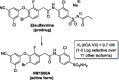
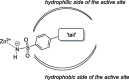
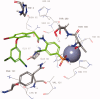
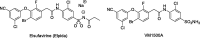Biochemical profiling of anti-HIV prodrug Elsulfavirine (Elpida®) and its active form VM1500A against a panel of twelve human carbonic anhydrase isoforms
- PMID: 34000969
- PMCID: PMC8143618
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2021.1927007
Biochemical profiling of anti-HIV prodrug Elsulfavirine (Elpida®) and its active form VM1500A against a panel of twelve human carbonic anhydrase isoforms
Abstract
The non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor VM1500A is approved for the treatment of HIV/AIDS in its N-acyl sulphonamide prodrug form elsulfavirine (Elpida®). Biochemical profiling against twelve human carbonic anhydrase (CA, EC 4.2.1.1) isoforms showed that while elsulfavirine was a weak inhibitor of all isoforms, VM1500A potently and selectively inhibited human (h) hCA VII isoform, a proven target for the therapy of neuropathic pain. The latter is a common neurologic complication of HIV infection and we hypothesise that by using Elpida® in patients may help alleviate this debilitating symptom.
Keywords: N-acyl sulphonamide prodrug; Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor; elsulfavirine; human carbonic anhydrase; isoform selectivity; neuropathic pain.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Zhan P, Pannecouque C, De Clercq E, Liu X.. Anti-HIV drug discovery and development: current innovations and future trends. J Med Chem 2016;59:2849–78. - PubMed
-
- Al-Salama ZT. Elsulfavirine: first global approval. Drugs 2017;77:1811–6. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, De Clercq E, Li G.. Current and emerging non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) for HIV-1 treatment. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 2019;15:813–29. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical