Nomogram for predicting preoperative regional lymph nodes metastasis in patients with metaplastic breast cancer: a SEER population-based study
- PMID: 34001061
- PMCID: PMC8130108
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-08313-6
Nomogram for predicting preoperative regional lymph nodes metastasis in patients with metaplastic breast cancer: a SEER population-based study
Abstract
Background: Metaplastic breast cancer (MBC) is a rare subtype of breast cancer, and generally associated with poor outcomes. Lymph nodes metastasis (LNM) is confirmed as a critical independent prognostic factor and determine the optimal treatment strategies in MBC patients. We aimed to develop and validate a nomogram to predict the possibility of preoperative regional LNM in MBC patients.
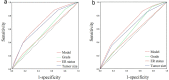
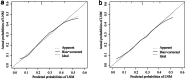
Methods: MBC patients diagnosed between 1990 and 2016 in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database were included and stochastically divided into a training set and validation set at a ratio of 7:3. The risk variables of regional LNM in the training set were determined by univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses. And then we integrated those risk factors to construct the nomogram. The prediction nomogram was further verified in the verification set. The discrimination, calibration and clinical utility of the nomogram were evaluated by the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC), calibration plots and decision curve analysis (DCA), respectively.
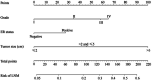
Results: A total of 2205 female MBC patients were included in the study. Among the 2205 patients, 24.8% (546/2205) had positive regional lymph nodes. The nomogram for predicting the risk of regional LNM contained predictors of grade, estrogen receptor (ER) status and tumor size, with AUC of 0.683 (95% confidence interval (CI): 0.653-0.713) and 0.667 (95% CI: 0.621-0.712) in the training and validation sets, respectively. Calibration plots showed perfect agreement between actual and predicted regional LNM risks. At the same time, DCA of the nomogram demonstrated good clinical utilities.
Conclusions: The nomogram established in this study showed excellent prediction ability, and could be used to preoperatively estimate the regional LNM risk in MBC.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Lymph nodes metastasis; Metaplastic breast cancer; Nomogram; SEER.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared no conflicts of interest among them.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nomogram for predicting preoperative lymph node involvement in patients with invasive micropapillary carcinoma of breast: a SEER population-based study.BMC Cancer. 2018 Nov 8;18(1):1085. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4982-5. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30409127 Free PMC article.
-
Novel nomograms to predict lymph node metastasis and liver metastasis in patients with early colon carcinoma.J Transl Med. 2019 Jun 10;17(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-1940-1. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31182111 Free PMC article.
-
A novel nomogram and risk classification system for predicting lymph node metastasis of breast mucinous carcinoma: A SEER-based study.Cancer Med. 2022 Dec;11(24):4767-4783. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4804. Epub 2022 May 22. Cancer Med. 2022. PMID: 35599552 Free PMC article.
-
The predictive value of machine learning and nomograms for lymph node metastasis of prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2023 Sep;26(3):602-613. doi: 10.1038/s41391-023-00704-z. Epub 2023 Jul 24. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2023. PMID: 37488275
-
A nomogram for predicting the 4-year risk of chronic kidney disease among Chinese elderly adults.Int Urol Nephrol. 2023 Jun;55(6):1609-1617. doi: 10.1007/s11255-023-03470-y. Epub 2023 Jan 31. Int Urol Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36720744 Review.
Cited by
-
Low RUFY3 expression level is associated with lymph node metastasis in older women with invasive breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2022 Feb;192(1):19-32. doi: 10.1007/s10549-021-06482-3. Epub 2022 Jan 12. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2022. PMID: 35018543 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of prognostic model for postoperative patients with metaplastic breast cancer: Based on a retrospective large data analysis and Chinese multicenter study.Front Genet. 2022 Aug 25;13:993116. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.993116. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36092916 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer: a study based on the SEER database.Clin Exp Med. 2025 Mar 13;25(1):82. doi: 10.1007/s10238-025-01591-5. Clin Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 40080204 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and validation of prognostic nomogram for metaplastic breast cancer.Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2022 Feb 1;22(1):131-139. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2021.5911. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 34247567 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and validation of the survival prediction risk model for appendiceal cancer.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 28;9:1022595. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1022595. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36388937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huvos AG, Lucas JC, Jr, Foote FW., Jr Metaplastic breast carcinoma. Rare form of mammary cancer. N Y State J Med. 1973;73(9):1078–1082. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

