Changes to body mass index, work self-efficacy, health-related quality of life, and work participation in people with obesity after vocational rehabilitation: a prospective observational study
- PMID: 34001067
- PMCID: PMC8130265
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-021-10954-y
Changes to body mass index, work self-efficacy, health-related quality of life, and work participation in people with obesity after vocational rehabilitation: a prospective observational study
Abstract
Background: People on or at risk of sick leave from work due to obesity or obesity-related problems participated in a new vocational rehabilitation (VR). The study aimed to examine the outcome changes in the participants' health-related quality of life (HRQoL), body mass index (BMI), return to work self-efficacy (RTWSE), work ability scale (WAS) and degree of work participation (DWP) after their participation in the 12-month VR programme. The secondary aim was to examine associations between the outcome changes and HRQoL at 12-month follow-up, measured with the HRQoL 15D instrument (15D).
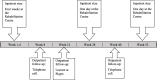
Methods: This prospective observational study included 95 participants. The one-year multidisciplinary VR programme with an integrated work and lifestyle intervention included 4 weeks of inpatient stay followed-up by 5 meetings. A paired sample t-test was used to examine changes in HRQoL, BMI, RTWSE, WAS, and DWP between baseline and the 12-month follow-up. Multiple linear regression analyses explored associations between changes in HRQoL and the outcome variables.
Results: The participants achieved statistically significant changes in HRQoL (2.57, 95% CI: 1.35 to 3.79), BMI (- 2.33, 95% CI: - 3.10 to - 1.56), RTWSE (15.89, 95% CI: 4.07 to 27.71), WAS (1.51, 95% CI: 0.83 to 2.20) and DWP (18.69, 95% CI: 8.35 to 29.02). At 12 months, a significant association was found between HRQoL and BMI (B = - 0.34, 95% CI: - 0.65 to - 0.04), RTWSE (B = 0.02, 95% CI: 0.004 to 0.04), WAS (B = 0.91, 95% CI: 0.55 to 1.28), DWP (B = - 0.02, 95% CI: - 0.04 to 0.001) and work absence (B = - 0.01, 95% CI: - 0.02 to - 0.002). The regression model explained 71.8% of the HRQoL variance.
Conclusion: The results indicated positive changes in HRQoL, BMI, RTWSE, WAS and DWP from baseline to the 12-month follow-up. Factors associated with HRQoL at the 12-month follow-up were decreased BMI, increased RTWSE, improved WAS and reduced work absence. Future studies examining VR programmes with lifestyle interventions for people with obesity are recommended.
Trial registration: Norwegian Regional Committee for Medical and Health Research Ethics (REC) 2017/573, Clinical Trials NCT03286374 , registered 18. September 2017. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?cond=Obesity&term=Anita+Dyb+Linge&cntry=NO&state=&city=&dist=.
Keywords: Health-related quality of life; Obesity; Return to work self-efficacy; Vocational rehabilitation; Work ability; Work absence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this study.
Figures
References
-
- Colditz GA, Dart H. Epidemiology and health and economic consequences. In: Wadden TA, Bray G, editors. Handbook of obesity treatment. 2. New York: Guildford Press; 2018. pp. 3–24.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical